Key takeaways:
~ Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organ systems in the body.
~Research shows that there is a hereditary component to lupus, and genes combine with environmental triggers to cause the disease.
~ Understanding your genetic variants can shed some light on what is going on with your body’s immune system.
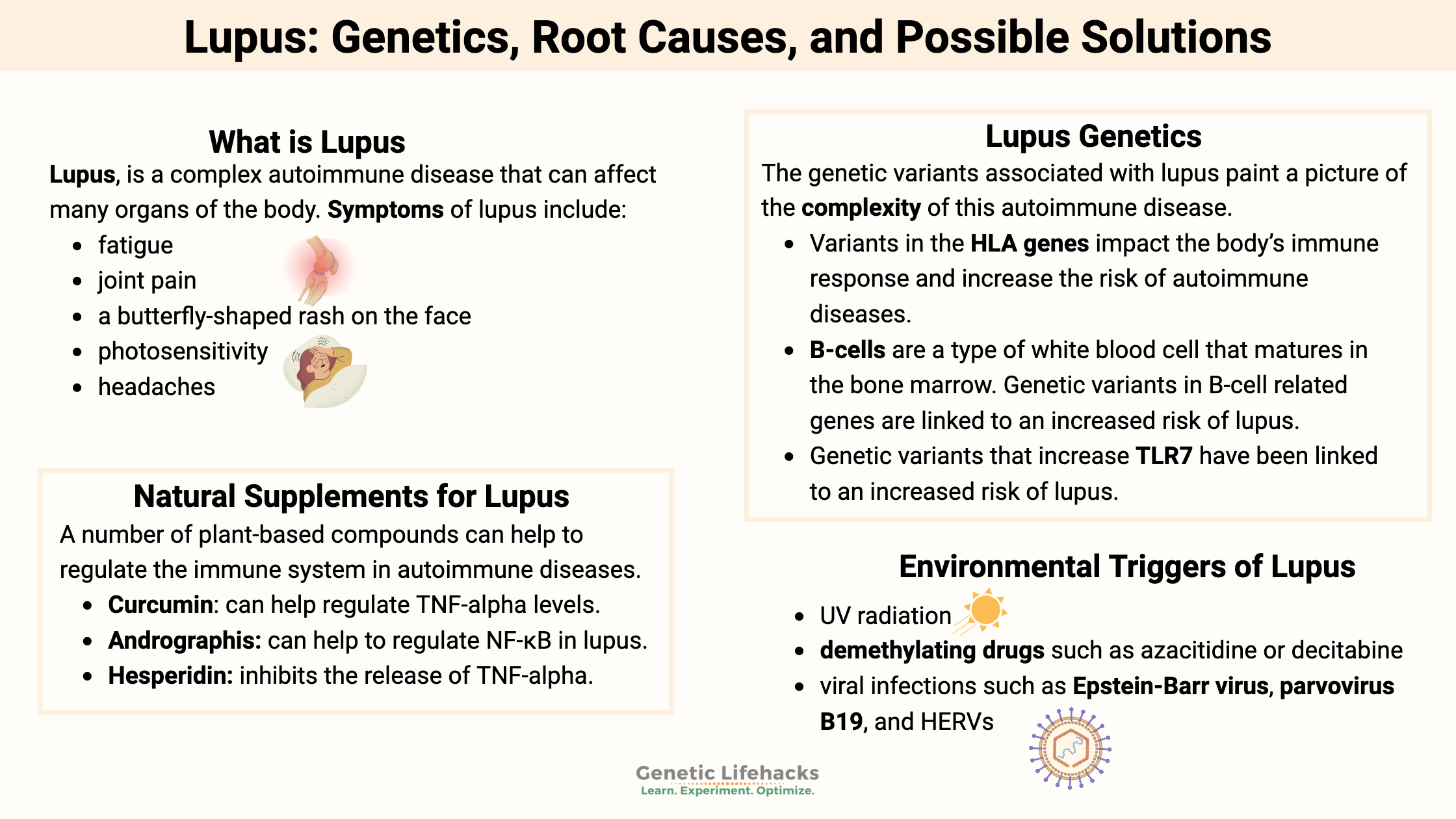
Lupus, a systemic autoimmune disease
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), often just called lupus, is a complex autoimmune disease that can affect many different organs of the body.
The Lupus Foundation of America estimates that 1.5 million people in the U.S. have lupus. It affects mainly women of childbearing age, although men and children can get lupus as well.[ref]
Ethnicity is an important risk factor as well. African American women have a three- to fourfold greater risk of lupus.[ref]
Common signs and symptoms of lupus include:
- fatigue
- joint pain
- a butterfly-shaped rash on the face
- photosensitivity
- headaches
As an autoimmune disease, the hyperactivation of the immune response causes excess proinflammatory cytokines. It, in turn, leads to the activation of immune factors such as B cells and T cells.[ref]
Is lupus genetic?
Lupus is thought to have both genetic and environmental components.
Genetic research shows that there isn’t a single gene that causes lupus. Instead, researchers have identified a bunch of different genetic variants that increase the relative risk of lupus a bit.
The genetic component of lupus is estimated to be 25-40%.[ref] People with a close relative with lupus are at a 20-fold increased risk relative to the rest of the population.[ref]
The genetic variants associated with lupus paint a picture of the complexity of this autoimmune disease.
- Variants in the HLA genes impact the body’s immune response and increase the risk of autoimmune diseases.
- B-cells are a type of white blood cell that matures in the bone marrow. Increased numbers of memory B-cells increase the risk of lupus and autoimmune diseases. Genetic variants in B-cell-related genes are linked to an increased risk of lupus.[ref]
- Genes in the interferon pathway point to the role that genetically increased interferon plays in lupus.[ref]
- Genetic variants that increase TLR7 have been linked to an increased risk of lupus.[ref] TLR7 detects viral RNA strands and activates interferon pathways.
- Rare mutations in the UNC93B1, which increase TLR7, have been detected in early-onset lupus.[ref]
Interferon-α is a cytokine that cells release, signaling a need for the immune system to be activated.
Generally, interferon is elevated and activated by viral pathogens. Interferon acts both as an immune signal and as a way to interfere (thus the name interferon) with viral replication. In lupus, interferon-α is often elevated, starting the cascade of autoimmune events.[ref]
Genetic susceptibility plus a trigger = lupus
Most people with genetic variants linked to lupus will not end up with the disease.
In addition to genetic risk, many environmental factors increase the risk of developing lupus.
Environmental triggers of lupus include[ref]:
- UV radiation
- demethylating drugs such as azacitidine or decitabine
- viral infections such as Epstein-Barr virus, parvovirus B19, and HERVs[ref]
Epstein-Barr Virus:
Research shows that there is an increased risk of lupus with IgA for a specific viral protein in EBV. CD40 genetic variants affect susceptibility to lupus in conjunction with EBV.[ref]
A 2025 study showed that EBV-infected B cells can activate helper T cells, which causes a chain reaction where the T cells activate uninfected B cells. This then drives a systemic autoimmune response, such as what is seen in lupus. [ref]
Related article: Epstein-Barr Virus: Genetic Risks, Reactivation, and Chronic Illnesses
Microplastics, joints, and inflammation:
In addition to the well-known viral and drug causes of lupus, animal studies show that microplastics or nanoplastics that are absorbed into the body likely play a role in the joint inflammation in lupus. The researchers added microplastics to the animals’ water and found that they ended up causing synovial damage in the joints in a mouse model of lupus. Essentially, the microplastics increased oxidative stress and NF-kB signaling in the joints, which disrupted the structure and function.[ref]
Related article: Microplastics Research Roundup
Below is just a (partial) list of genes that have been studied in lupus patients. If you have lupus, I hope that understanding the genetic links can help you target the right solutions.
Lupus Genotype Report
Access this content:
An active subscription is required to access this content.
Lifehacks: Diet and supplements for lupus
The following are research-backed options that may help with lupus symptoms. Talk with your doctor – especially if you are on any medications – before adding in any immune system modifiers.
Boosting Melatonin:
More than just a ‘sleep hormone’, melatonin is important in your immune system. It helps increase the immune response against pathogens, but it also helps to moderate an overactive immune response.[ref]
Lifestyle changes to boost melatonin:
Melatonin is your body’s natural immune modulator, produced in large amounts overnight.
Light at night in the blue wavelengths (~480nm) blocks melatonin production. Blue light is abundant in our modern world, especially from electronics and LED lights.
Blocking blue light at night raises melatonin production by around 50% on average, which is significant. Two ways to increase melatonin:
- Stop using electronics (TV, phone, tablets, laptops) at night and turn the house lights down low by using lamps with warm colored bulb.
- Blue-blocking glasses that block 100% of blue light (the 100% part is important).
Sleeping in a dark room is also important. Light can come through your eyelids at night, impacting melatonin production. Blackout curtains or shades can make a big difference, and make sure there aren’t any glowing green or blue indicator lights (like from a laptop charger) in your room at night.
Another option is to try a low-dose, timed-release melatonin supplement.
Natural supplements that impact the immune response in lupus and autoimmune diseases:
Access this content:
An active subscription is required to access this content.
Related Articles and Topics:
HLA-B27: Genetic Variant That Increases Susceptibility to Autoimmune Diseases
TNF-alpha: Inflammation, Chronic Diseases, and Genetic Susceptibility
HLA-B27: Genetic Variant That Increases Susceptibility to Autoimmune Diseases
References:
“5 Foods and Medications to Avoid If You Have Lupus : Johns Hopkins.” Johns Hopkins Lupus Center, https://www.hopkinslupus.org/lupus-info/lifestyle-additional-information/avoid/. Accessed 10 Dec. 2021.
Aggarwal, Bharat B., et al. “Curcumin: An Orally Bioavailable Blocker of TNF and Other pro-Inflammatory Biomarkers.” British Journal of Pharmacology, vol. 169, no. 8, Aug. 2013, pp. 1672–92. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12131.
Armstrong, D. L., et al. “Identification of New SLE-Associated Genes with a Two-Step Bayesian Study Design.” Genes and Immunity, vol. 10, no. 5, July 2009, pp. 446–56. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.38.
Balkrishna, Acharya, et al. “Mechanistic Paradigms of Natural Plant Metabolites as Remedial Candidates for Systemic Lupus Erythromatosus.” Cells, vol. 9, no. 4, Apr. 2020, p. 1049. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041049.
—. “Mechanistic Paradigms of Natural Plant Metabolites as Remedial Candidates for Systemic Lupus Erythromatosus.” Cells, vol. 9, no. 4, Apr. 2020, p. 1049. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041049.
—. “Mechanistic Paradigms of Natural Plant Metabolites as Remedial Candidates for Systemic Lupus Erythromatosus.” Cells, vol. 9, no. 4, Apr. 2020, p. 1049. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041049.
Blanco, P., et al. “Induction of Dendritic Cell Differentiation by IFN-Alpha in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.” Science (New York, N.Y.), vol. 294, no. 5546, Nov. 2001, pp. 1540–43. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1064890.
Calise, Justine, et al. “Lineage-Specific Functionality of an Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 Lupus Risk Haplotype: Lack of B Cell Intrinsic Effects.” Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 9, May 2018, p. 996. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00996.
Chung, Sharon A., et al. “Differential Genetic Associations for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on Anti–DsDNA Autoantibody Production.” PLoS Genetics, vol. 7, no. 3, Mar. 2011, p. e1001323. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1001323.
—. “Differential Genetic Associations for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on Anti–DsDNA Autoantibody Production.” PLoS Genetics, vol. 7, no. 3, Mar. 2011, p. e1001323. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1001323.
Crow, Mary K. “Type I Interferon in the Pathogenesis of Lupus.” The Journal of Immunology, vol. 192, no. 12, June 2014, pp. 5459–68. www.jimmunol.org, https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1002795.
Dieudé, P., et al. “Association of the TNFAIP3 Rs5029939 Variant with Systemic Sclerosis in the European Caucasian Population.” Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, vol. 69, no. 11, Nov. 2010, pp. 1958–64. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.127928.
Fan, Ye, et al. “Association of BLK (Rs13277113, Rs2248932) Polymorphism with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis.” Molecular Biology Reports, vol. 38, no. 7, Oct. 2011, pp. 4445–53. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0573-5.
—. “Association of BLK (Rs13277113, Rs2248932) Polymorphism with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis.” Molecular Biology Reports, vol. 38, no. 7, Oct. 2011, pp. 4445–53. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0573-5.
Fernando, Michelle M. A., et al. “Identification of Two Independent Risk Factors for Lupus within the MHC in United Kingdom Families.” PLoS Genetics, vol. 3, no. 11, Nov. 2007, p. e192. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0030192.
Ghodke-Puranik, Yogita, and Timothy B. Niewold. “Immunogenetics of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Comprehensive Review.” Journal of Autoimmunity, vol. 64, Nov. 2015, pp. 125–36. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2015.08.004.
—. “Immunogenetics of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Comprehensive Review.” Journal of Autoimmunity, vol. 64, Nov. 2015, pp. 125–36. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2015.08.004.
Gorman, Jacquelyn A., et al. “The A946T Variant IFIH1 RNA Sensor Mediates an Interferon Program That Limits Viral Infection but Increases the Risk for Autoimmunity.” Nature Immunology, vol. 18, no. 7, July 2017, pp. 744–52. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3766.
Guarnizo-Zuccardi, P., et al. “Cytokine Gene Polymorphisms in Colombian Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.” Tissue Antigens, vol. 70, no. 5, Nov. 2007, pp. 376–82. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0039.2007.00917.x.
Handono, Kusworini, et al. “Treatment of Low Doses Curcumin Could Modulate Th17/Treg Balance Specifically on CD4+ T Cell Cultures of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients.” Central-European Journal of Immunology, vol. 40, no. 4, 2015, pp. 461–69. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.5114/ceji.2015.56970.
Help Us Solve The Cruel Mystery | Lupus Foundation of America. https://www.lupus.org/. Accessed 10 Dec. 2021.
IRF5 Gene: MedlinePlus Genetics. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/gene/irf5/. Accessed 10 Dec. 2021.
Jones, Sarah A., et al. “Rare Variants in Non-Coding Regulatory Regions of the Genome That Affect Gene Expression in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.” Scientific Reports, vol. 9, Oct. 2019, p. 15433. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51864-9.
Kalergis, Alexis M., et al. “Modulation of Nuclear Factor-ΚB Activity Can Influence the Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.” Immunology, vol. 128, no. 1 Pt 2, Sept. 2009, pp. e306–14. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02964.x.
Karrar, Sarah, and Deborah S. Cunninghame Graham. “Abnormal B Cell Development in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.” Arthritis & Rheumatology (Hoboken, N.j.), vol. 70, no. 4, Apr. 2018, pp. 496–507. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40396.
Kelly, J. A., et al. “Interferon Regulatory Factor-5 Is Genetically Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in African Americans.” Genes and Immunity, vol. 9, no. 3, Apr. 2008, pp. 187–94. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.4.
Lee, Young Ho, and Gwan Gyu Song. “Associations between TNFAIP3 Gene Polymorphisms and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis.” Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers, vol. 16, no. 9, Sept. 2012, pp. 1105–10. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1089/gtmb.2012.0096.
Li, S. W., et al. “Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms of IRF8 Gene Are Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Chinese Han Population.” International Journal of Immunogenetics, vol. 41, no. 2, 2014, pp. 112–18. Wiley Online Library, https://doi.org/10.1111/iji.12087.
Lin, Gu-Jiun, et al. “Modulation by Melatonin of the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 14, no. 6, May 2013, pp. 11742–66. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140611742.
Liu, Hui-Feng, et al. “Association of Rs10954213 Polymorphisms and Haplotype Diversity in Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis.” Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Medical Sciences = Hua Zhong Ke Ji Da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ying De Wen Ban = Huazhong Keji Daxue Xuebao. Yixue Yingdewen Ban, vol. 33, no. 1, Feb. 2013, pp. 15–21. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1064-4.
Mariella, Elisa, et al. “The Length of the Expressed 3′ UTR Is an Intermediate Molecular Phenotype Linking Genetic Variants to Complex Diseases.” Frontiers in Genetics, vol. 10, Aug. 2019, p. 714. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00714.
Nashi, Emil, et al. “The Role Of B Cells in Lupus Pathogenesis.” The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, vol. 42, no. 4, Apr. 2010, pp. 543–50. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2009.10.011.
Niewold, Timothy B., et al. “Association of the IRF5 Risk Haplotype With High Serum Interferon-α Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients.” Arthritis and Rheumatism, vol. 58, no. 8, Aug. 2008, pp. 2481–87. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1002/art.23613.
Quaglia, Marco, et al. “Viral Infections and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: New Players in an Old Story.” Viruses, vol. 13, no. 2, Feb. 2021. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020277.
Ramírez-Bello, Julian, et al. “BLK and BANK1 Polymorphisms and Interactions Are Associated in Mexican Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.” Inflammation Research: Official Journal of the European Histamine Research Society … [et Al.], vol. 68, no. 8, Aug. 2019, pp. 705–13. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-019-01253-9.
Scrivo, Rossana, et al. “The Role of Dietary Sodium Intake on the Modulation of T Helper 17 Cells and Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.” PLoS ONE, vol. 12, no. 9, 2017. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184449.
Sigurdsson, Snaevar, et al. “A Risk Haplotype of STAT4 for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Is Over-Expressed, Correlates with Anti-DsDNA and Shows Additive Effects with Two Risk Alleles of IRF5.” Human Molecular Genetics, vol. 17, no. 18, Sept. 2008, pp. 2868–76. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddn184.
Skonieczna, Katarzyna, et al. “Genetic Similarities and Differences between Discoid and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients within the Polish Population.” Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii, vol. 34, no. 3, June 2017, pp. 228–32. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.5114/pdia.2017.67479.
Song, G. G., and Y. H. Lee. “Association between BLK Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to SLE : A Meta-Analysis.” Zeitschrift Fur Rheumatologie, vol. 76, no. 2, Mar. 2017, pp. 176–82. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-016-0072-8.
—. “Association between BLK Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to SLE : A Meta-Analysis.” Zeitschrift Fur Rheumatologie, vol. 76, no. 2, Mar. 2017, pp. 176–82. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-016-0072-8.
TNXB Gene: MedlinePlus Genetics. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/gene/tnxb/. Accessed 10 Dec. 2021.
Williams, Edith M., et al. “Peer Approaches to Self-Management (PALS): Comparing a Peer Mentoring Approach for Disease Self-Management in African American Women with Lupus with a Social Support Control: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.” Trials, vol. 20, Aug. 2019, p. 529. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3580-4.
Zeng, Chang, et al. “B-Cell Lymphocyte Kinase Polymorphisms Rs13277113, Rs2736340, and Rs4840568 and Risk of Autoimmune Diseases: A Meta-Analysis.” Medicine, vol. 96, no. 36, Sept. 2017, p. e7855. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007855.
Zhang, Junlong, et al. “Autoimmune Disease Associated IFIH1 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Related with IL-18 Serum Levels in Chinese Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients.” Scientific Reports, vol. 8, June 2018, p. 9442. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27782-7.