Key takeaways:
~ The World Health Organization now estimates that almost 10% of couples worldwide are dealing with fertility issues.
~ The problems leading to infertility are equally split between males and females.[ref]
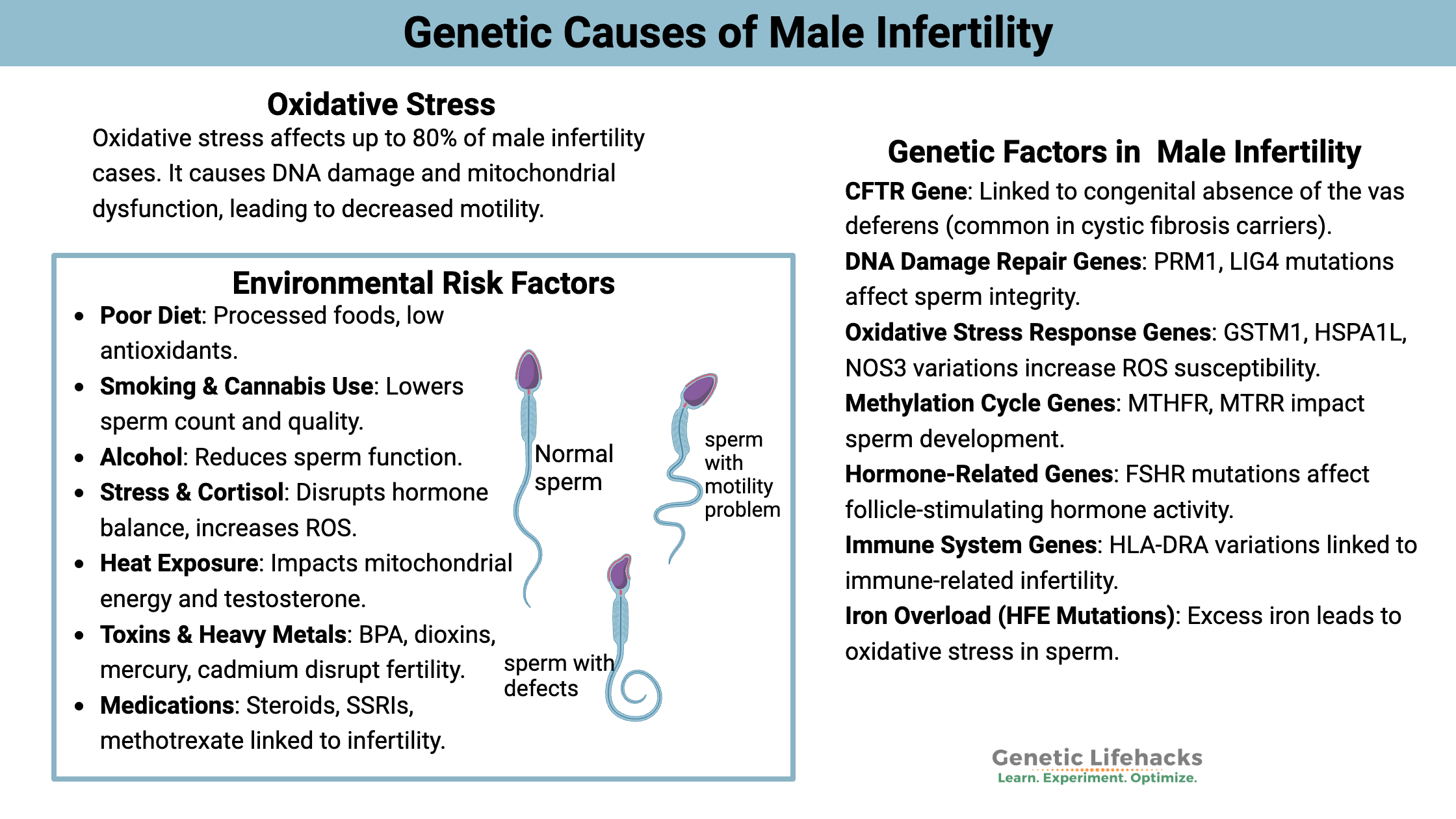
~ Many different genetic variants can increase the risk of infertility in men. These genes impact different aspects of sperm production – from hormones to oxidative stress to DNA damage repair.
Male Infertility: Getting to the root cause
Infertility is formally defined as an inability to become pregnant after 12 months of unprotected sex. Many factors influence infertility: genetic mutations, environmental exposure, physical abnormalities, and the combination of environmental factors with genetic susceptibility from common variants.
For most couples facing infertility, the first thing to do is go to a fertility specialist. The doctor can help rule out physical abnormalities or major hormone alterations.
But what happens when infertility is labeled ‘idiopathic’, which is medical speak for ‘unknown origin’? That is when you need to dig deeper into lifestyle and genetic susceptibility.
How is sperm produced?
Men produce sperm constantly through a process called spermatogenesis. On average, hundreds of millions of precursor sperm cells are generated daily in the seminiferous tubules. From there, they go through a series of events, resulting in mature spermatozoa that are stored in the epididymis.
The whole process takes around three months. This time scale of three months is important when you are experimenting with lifestyle changes to make a difference for infertility. Patience, along with targeted interventions, are key.[ref]
What goes wrong with sperm?
When you start reading the research on male infertility causes, you’ll come across several technical terms for defining alterations in sperm concentration and motility.
According to the WHO, abnormal sperm function is defined as:[ref]
- oligozoospermia = decreased sperm concentration (defined as < 15 ×106 sperm/ml)
- asthenozoospermia = decreased sperm motility (progressive motility <32% or total sperm mobility under 40%)
- teratospermia = majorly decreased sperm motility (sperm motility of <4%)
- oligoasthenoteratozoospermia = combination of all of the above
Essentially, this boils down to not having enough healthy sperm or not having enough sperm motility. Or both.
Oxidative Stress: Lifestyle, diet, inflammation
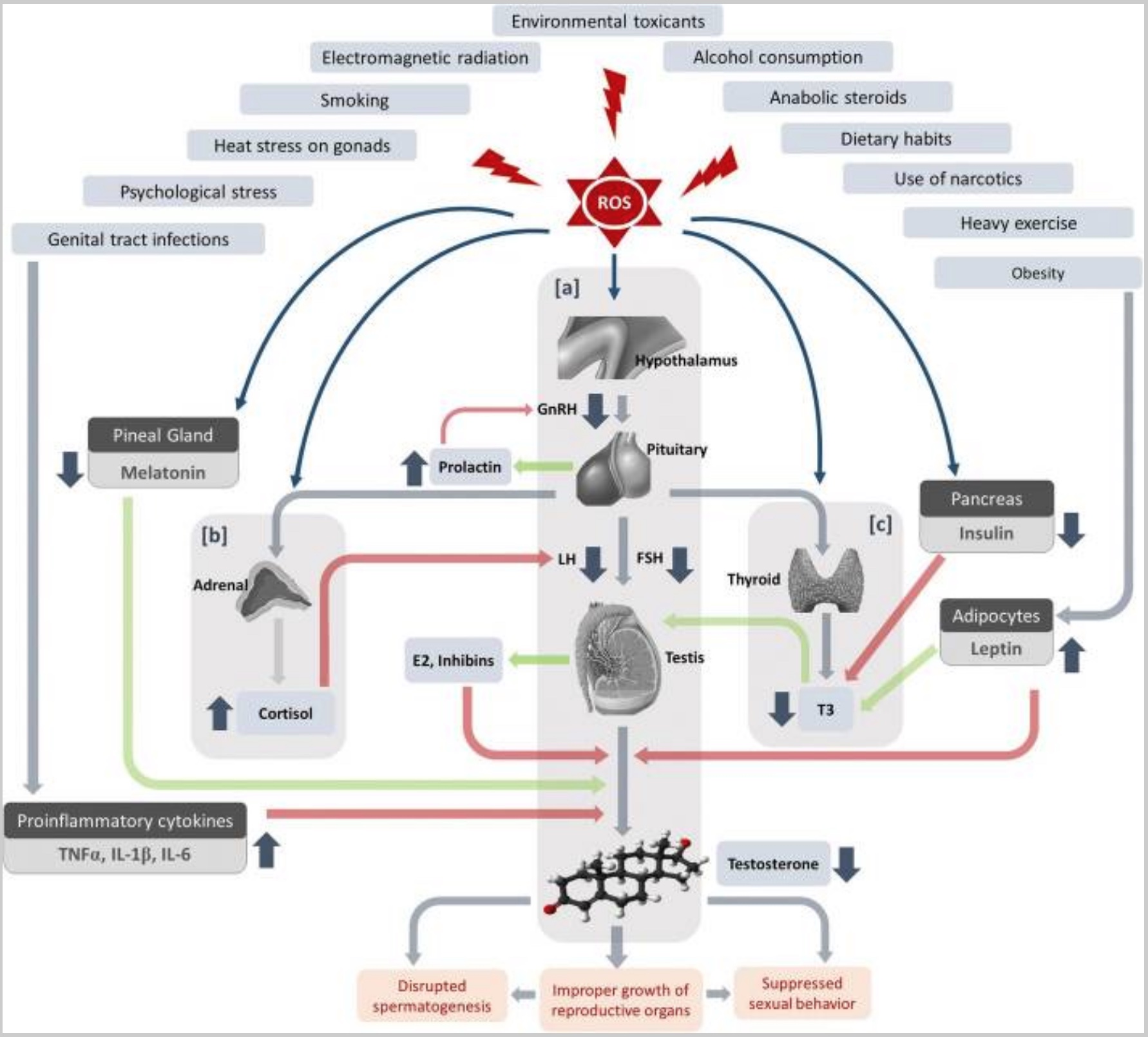
Research shows that one of the most significant sources of male infertility is oxidative stress, accounting for about half (somewhere between 30-80%)
Oxidative stress is defined as cells producing more reactive oxygen species (ROS) than they can balance out with antioxidants.[ref]
Sperm are particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress because the cell membranes are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, which are more prone to oxidation when ROS is out of balance.[ref]
Excess ROS can also damage DNA in sperm, which is more of a problem than in normal cells due to a lack of enzymes to combat oxidative stress.[ref]
One research study states:
“The oxidative stress, which refers to an imbalance in levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants, is one of the main causes of infertility in men.”[ref]
For motility, sperm need a lot of energy and thus have a lot of mitochondria in the flagellum. Excess oxidative stress impairs the mitochondria, leading to decreased motility.[ref]
Sources of oxidative stress (environmental causes):
Poor diet:
A diet of fast food, junk food, and beer is a recipe for male infertility. Not only is your body fighting against the additives and oxidized fats in junk food, but the antioxidants from vegetables or organ meats are needed for fighting oxidative stress.
Cigarette smoking:
Smoking is associated with reduced sperm count and decreased sperm quality.[ref] Cannabis use is also linked to reduced sperm count and an increase in abnormal sperm.[ref]
Excessive alcohol consumption:
Alcohol consumption is also linked to decreased sperm function in men with infertility.[ref]
Stress/ cortisol / HPA axis alterations:
High levels of ROS not only lead to oxidative stress but also cause a disruption in male sex hormones via the HPA axis. Additionally, stress causes HPA axis alterations and increases inflammatory cytokines. Thus, stress can cause infertility in two ways: social/psychological stress or physical stress caused by ROS.[ref][ref]
Heat stress:
Excessive heat in the testes increases oxidative stress and disrupts mitochondrial energy production. It can also decrease testosterone and luteinizing hormone levels. Heat stress also impacts the HPA axis and hormone levels.[ref]
Environmental toxicants:
Exposure to mercury, cadmium, BPA, and dioxin are all linked to infertility. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals may also be a problem for some men.[ref]
Hormone alterations:
Men with infertility, on average, have higher estradiol levels. Estradiol is a type of estrogen. Essentially, higher estrogen levels lead to a decrease in spermatogenesis.[ref] Higher estrogen levels could be due to obesity, conversion of testosterone to estrogen, or estrogen-mimicking chemicals.
Rare mutations in the androgen receptor gene can also cause infertility.[ref]
Other Lifestyle / Environmental Causes:
Obesity:
“… obesity is associated with male infertility, likely because of hormonal changes secondary to excess adipose tissue. In a retrospective multi-institutional cohort study, Bieniek et al. demonstrated an inverse relationship between body mass index (BMI) and testosterone, testosterone-to-estradiol ratio, ejaculate volume, sperm concentration, and morphology 6. The authors also reported higher rates of azoospermia and oligospermia among obese men (12.7% and 31.7%, respectively) compared with men of normal weight (9.8% and 24.5%) 6.”[ref]
Medications:
Certain drugs, such as anabolic steroids, SSRIs, methotrexate, cannabis, and sulfasalazine, are linked to a higher risk of infertility.[ref][ref][ref] If you are on prescription medication, talk with your doctor about infertility as a side effect.
Varicoceles:
Abnormally dilated and twisted veins in the pampiniform plexus, are a common cause of male infertility. Varicoceles are present in ~15 to 20% of men and 35 to 40% of infertile men, thus doubling the risk of infertility.[ref]
Hyperglycemia:
High blood glucose levels reduce sperm. It is partly because of increased oxidative stress, but other changes to sperm function also are seen in men with diabetes.[ref]
Male Infertility Genotype Report:
Lifehacks:
Go to the doctor… it is the obvious first step and can help you rule out physical problems affecting sperm production. At-home sperm analysis kits are also available for men who can’t easily get to a doctor (or just won’t go).[ref] Your doctor can also do hormone testing to ensure everything is balanced. For example, FSH treatments are available if FSH is out of balance.[ref]
Let’s dig into the research on what else you can do to increase sperm motility and quality. Keep in mind that it can take several months to see the full effects of some of these changes.
Lifestyle and Diet: Research on improving sperm quality
Less junk, more whole foods:
A recent study showed that cutting out sugar and junk food and replacing it with a healthy diet improved sperm motility in just a few weeks.[ref] A systematic review of studies showed that diets including fish, seafood, poultry, whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and dairy were associated with better sperm quality parameters.[ref]
Keep ’em cool:
A study found that 30 minutes in a hot bath reduced sperm parameters. Interestingly, the results showed that intermittent baths (every three days) were worse than a hot bath every day.[ref] Additional sources of heat stress linked to infertility include fever, sauna, sitting or driving for a long time, using a laptop on the lap, and electric blankets.[ref]
Stop smoking:
Cigarette smoke is harmful to your sperm (and your lungs and heart). Cannabis also reduces sperm count and causes abnormalities in sperm morphology.[ref]
Monitor your blood glucose levels:
High blood glucose levels impair fertility. An inexpensive blood glucose monitor can help determine if your fasting blood glucose level is consistently average. Additionally, you could use it to see your body’s response to different meals.
Avoiding environmental estrogen mimics:
Epidemiological studies show that higher levels of endocrine disruptors are associated with lower sperm quality. Specifically, higher phthalate and BPA exposures are linked with disruption of sperm formation.[ref]
Moderate exercise:
Most studies show that moderate exercise is good, but vigorous exercise may actually decrease reproductive hormone levels.[ref]
Research on 12 supplements for decreasing oxidative stress in sperm:
Related Articles and Topics:
Dads matter: MTHFR variants in fathers affect miscarriage risk
References:
Alahmar, Ahmed T. “Role of Oxidative Stress in Male Infertility: An Updated Review.” Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences, vol. 12, no. 1, Mar. 2019, p. 4. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.4103/jhrs.JHRS_150_18.
—. “Role of Oxidative Stress in Male Infertility: An Updated Review.” Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences, vol. 12, no. 1, Mar. 2019, p. 4. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.4103/jhrs.JHRS_150_18.
Asadi, Fatemeh, et al. “A Survey of the Common Mutations and IVS8-Tn Polymorphism of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Gene in Infertile Men with Nonobstructive Azoospermia and CBAVD in Iranian Population.” Iranian Biomedical Journal, vol. 23, no. 2, Mar. 2019, p. 92. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.29252/.23.2.92.
Barati, Erfaneh, et al. “Oxidative Stress and Male Infertility: Current Knowledge of Pathophysiology and Role of Antioxidant Therapy in Disease Management.” Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences: CMLS, vol. 77, no. 1, Jan. 2020, pp. 93–113. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03253-8.
Boeri, Luca, et al. “Heavy Cigarette Smoking and Alcohol Consumption Are Associated with Impaired Sperm Parameters in Primary Infertile Men.” Asian Journal of Andrology, vol. 21, no. 5, Oct. 2019, p. 478. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.4103/aja.aja_110_18.
Cerván-Martín, Miriam, et al. “Genetic Landscape of Nonobstructive Azoospermia and New Perspectives for the Clinic.” Journal of Clinical Medicine, vol. 9, no. 2, Jan. 2020, p. E300. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020300.
Clavijo, Raul I., et al. “Varicoceles: Prevalence and Pathogenesis in Adult Men.” Fertility and Sterility, vol. 108, no. 3, Sept. 2017, pp. 364–69. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.06.036.
Cyrus, Ali, et al. “The Effect of Adjuvant Vitamin C after Varicocele Surgery on Sperm Quality and Quantity in Infertile Men: A Double Blind Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial.” International Braz J Urol: Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology, vol. 41, no. 2, Apr. 2015, pp. 230–38. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.02.07.
Darbandi, Mahsa, et al. “Reactive Oxygen Species and Male Reproductive Hormones.” Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology : RB&E, vol. 16, 2018. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-018-0406-2.
—. “Reactive Oxygen Species and Male Reproductive Hormones.” Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology : RB&E, vol. 16, 2018. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-018-0406-2.
—. “Reactive Oxygen Species and Male Reproductive Hormones.” Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology : RB&E, vol. 16, 2018. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-018-0406-2.
Fainberg, Jonathan, and James A. Kashanian. “Recent Advances in Understanding and Managing Male Infertility.” F1000Research, vol. 8, 2019. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.17076.1.
—. “Recent Advances in Understanding and Managing Male Infertility.” F1000Research, vol. 8, 2019. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.17076.1.
—. “Recent Advances in Understanding and Managing Male Infertility.” F1000Research, vol. 8, 2019. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.17076.1.
Ghasemi, Hadi, et al. “Polymorphisms of DNA Repair Genes XRCC1 and LIG4 and Idiopathic Male Infertility.” Systems Biology in Reproductive Medicine, vol. 63, no. 6, Dec. 2017, pp. 382–90. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1080/19396368.2017.1374488.
Gunel-Ozcan, Aysen, et al. “Hereditary Haemochromatosis Gene (HFE) H63D Mutation Shows an Association with Abnormal Sperm Motility.” Molecular Biology Reports, vol. 36, no. 7, Sept. 2009, pp. 1709–14. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9372-7.
Kohan, Leila, et al. “HSPA1L and HSPA1B Gene Polymorphisms and Haplotypes Are Associated with Idiopathic Male Infertility in Iranian Population.” European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology, vol. 240, Sept. 2019, pp. 57–61. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2019.06.014.
La Vignera, Sandro, et al. “Diabetes Mellitus and Sperm Parameters.” Journal of Andrology, vol. 33, no. 2, Apr. 2012, pp. 145–53. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.111.013193.
Luo, Hongcheng, et al. “Associations of Serum Estradiol Level, Serum Estrogen Receptor-Alpha Level, and Estrogen Receptor-Alpha Polymorphism with Male Infertility: A Retrospective Study.” Medicine, vol. 100, no. 29, July 2021, p. e26577. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000026577.
Luo, Jun, et al. “[Relationship between the FSHR Thr307Ala-Asn680Ser gene polymorphism and male infertility: A meta-analysis].” Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue = National Journal of Andrology, vol. 23, no. 12, Dec. 2017, pp. 1121–26.
Majzoub, Ahmad, and Ashok Agarwal. “Systematic Review of Antioxidant Types and Doses in Male Infertility: Benefits on Semen Parameters, Advanced Sperm Function, Assisted Reproduction and Live-Birth Rate.” Arab Journal of Urology, vol. 16, no. 1, Mar. 2018, p. 113. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aju.2017.11.013.
—. “Systematic Review of Antioxidant Types and Doses in Male Infertility: Benefits on Semen Parameters, Advanced Sperm Function, Assisted Reproduction and Live-Birth Rate.” Arab Journal of Urology, vol. 16, no. 1, Mar. 2018, p. 113. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aju.2017.11.013.
Marques-Pinto, André, and Davide Carvalho. “Human Infertility: Are Endocrine Disruptors to Blame?” Endocrine Connections, vol. 2, no. 3, Sept. 2013, p. R15. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-13-0036.
Nätt, Daniel, et al. “Human Sperm Displays Rapid Responses to Diet.” PLoS Biology, vol. 17, no. 12, Dec. 2019. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000559.
Nemati, Houshang, et al. “Evaluation of the Association between Polymorphisms of PRM1 and PRM2 and the Risk of Male Infertility: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression.” Scientific Reports, vol. 10, no. 1, Oct. 2020, p. 17228. www.nature.com, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-74233-3.
Rahman, Sajid Ur, et al. “Therapeutic Role of Green Tea Polyphenols in Improving Fertility: A Review.” Nutrients, vol. 10, no. 7, June 2018, p. E834. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070834.
Ren, Zheng-Ju, et al. “Contribution of MTR A2756G Polymorphism and MTRR A66G Polymorphism to the Risk of Idiopathic Male Infertility.” Medicine, vol. 98, no. 51, Dec. 2019, p. e18273. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000018273.
Sadeghzadeh, F., et al. “Vitamin C Ameliorates the Adverse Effects of Dexamethasone on Sperm Motility, Testosterone Level, and Spermatogenesis Indexes in Mice.” Human & Experimental Toxicology, vol. 38, no. 4, Apr. 2019, pp. 409–18. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327118816137.
Safarinejad, Mohammad Reza, et al. “The Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (ENOS) T-786C, G894T, and 4a/b Gene Polymorphisms in the Risk of Idiopathic Male Infertility.” Molecular Reproduction and Development, vol. 77, no. 8, Aug. 2010, pp. 720–27. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.21210.
“Semen Abnormalities with SSRI Antidepressants.” Prescrire International, vol. 24, no. 156, Jan. 2015, pp. 16–17.
Sharma, Reecha, et al. “Cigarette Smoking and Semen Quality: A New Meta-Analysis Examining the Effect of the 2010 World Health Organization Laboratory Methods for the Examination of Human Semen.” European Urology, vol. 70, no. 4, Oct. 2016, pp. 635–45. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.04.010.
Simoni, Manuela, et al. “Prospects for FSH Treatment of Male Infertility.” The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, vol. 105, no. 7, July 2020, p. dgaa243. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa243.
Tvrda, Eva, et al. “Iron and Copper in Male Reproduction: A Double-Edged Sword.” Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, vol. 32, no. 1, Jan. 2015, p. 3. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-014-0344-7.
Wu, Wei, et al. “GSTM1 and GSTT1 Null Polymorphisms and Male Infertility Risk: An Updated Meta-Analysis Encompassing 6934 Subjects.” Scientific Reports, vol. 3, no. 1, July 2013, p. 2258. www.nature.com, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02258.
Yang, Y., et al. “Association between C677T and A1298C Polymorphisms of the MTHFR Gene and Risk of Male Infertility: A Meta-Analysis.” Genetics and Molecular Research: GMR, vol. 15, no. 2, Apr. 2016. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15027631.
Yu, Jianhong, et al. “Relationship between Common ENOS Gene Polymorphisms and Predisposition to Coronary Artery Disease: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis of 155 Published Association Studies.” Genomics, vol. 112, no. 3, May 2020, pp. 2452–58. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.01.019.
Zhang, Yi-Qing, et al. “Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Polymorphisms in Atrial Fibrillation: A PRISMA-Compliant Meta-Analysis.” Medical Science Monitor: International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research, vol. 25, Apr. 2019, pp. 2687–94. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.913528.