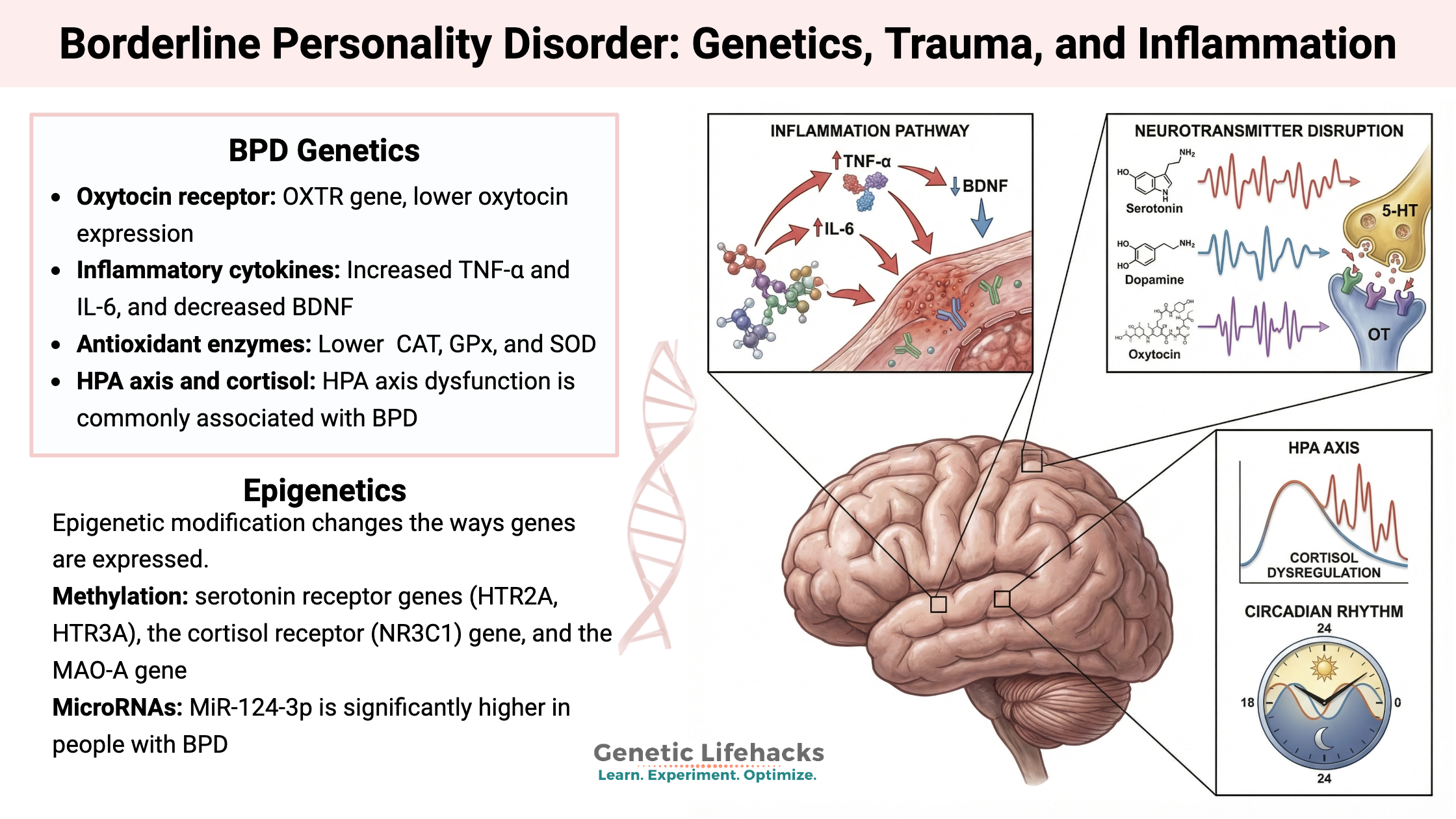
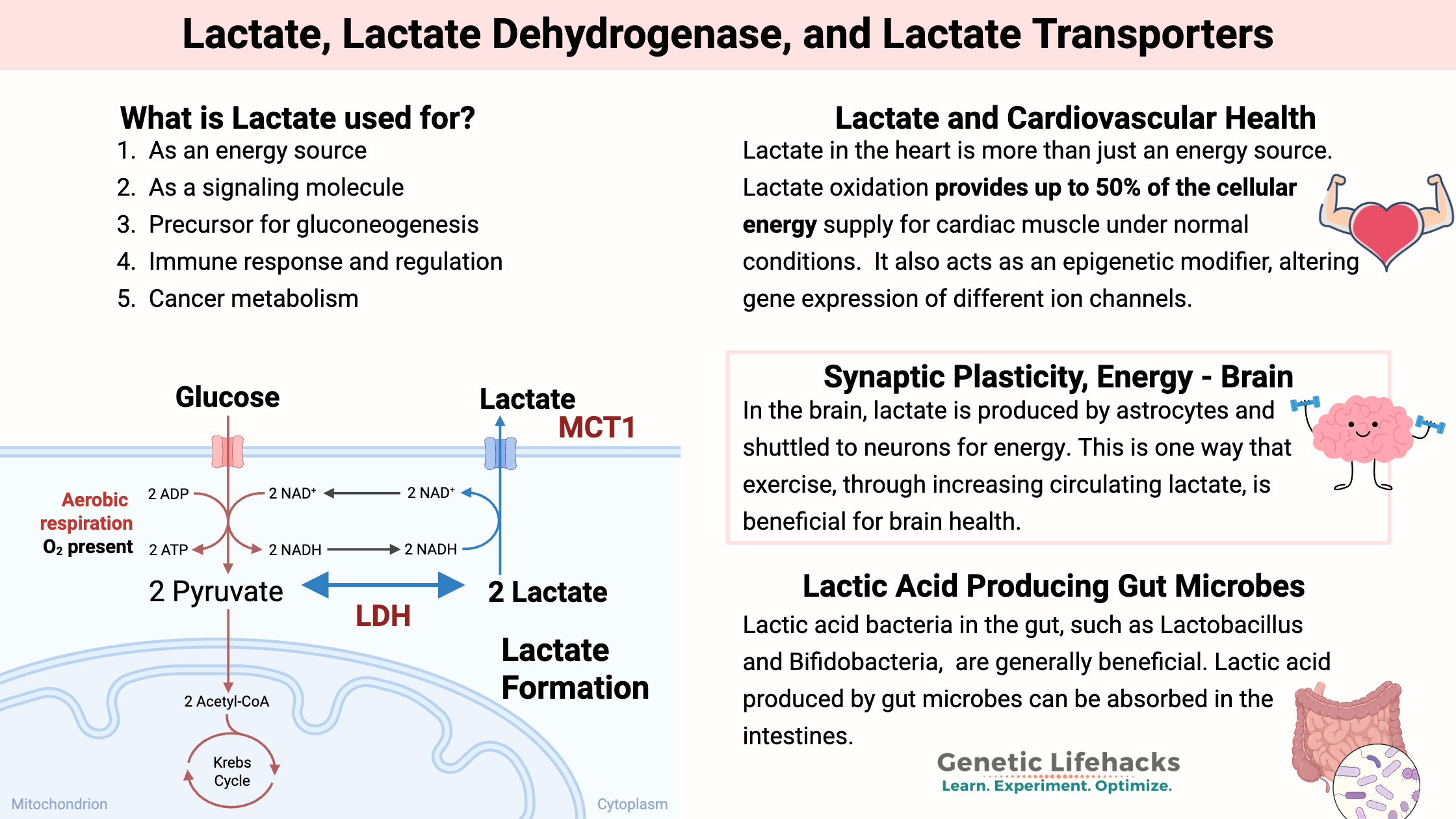
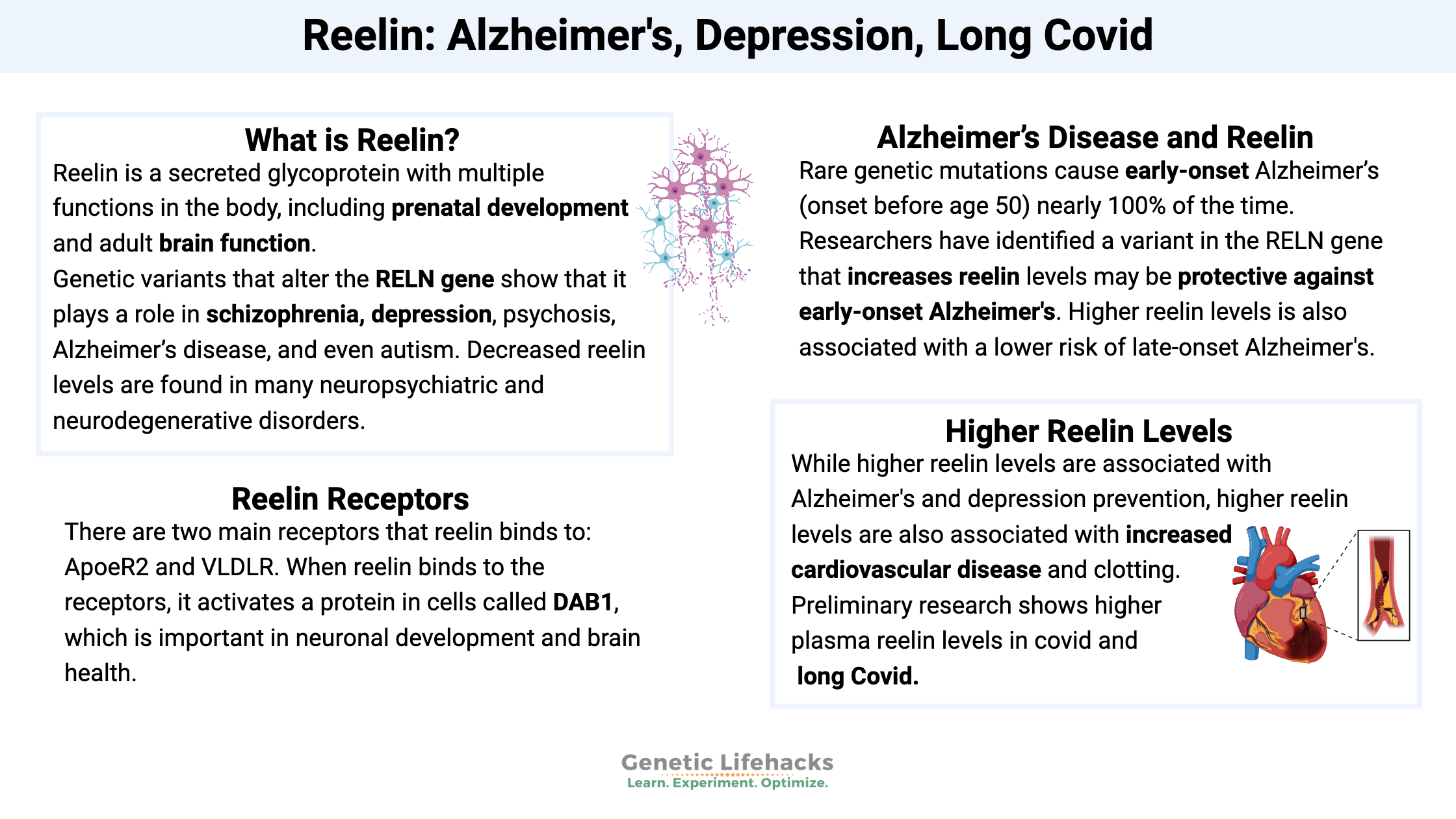
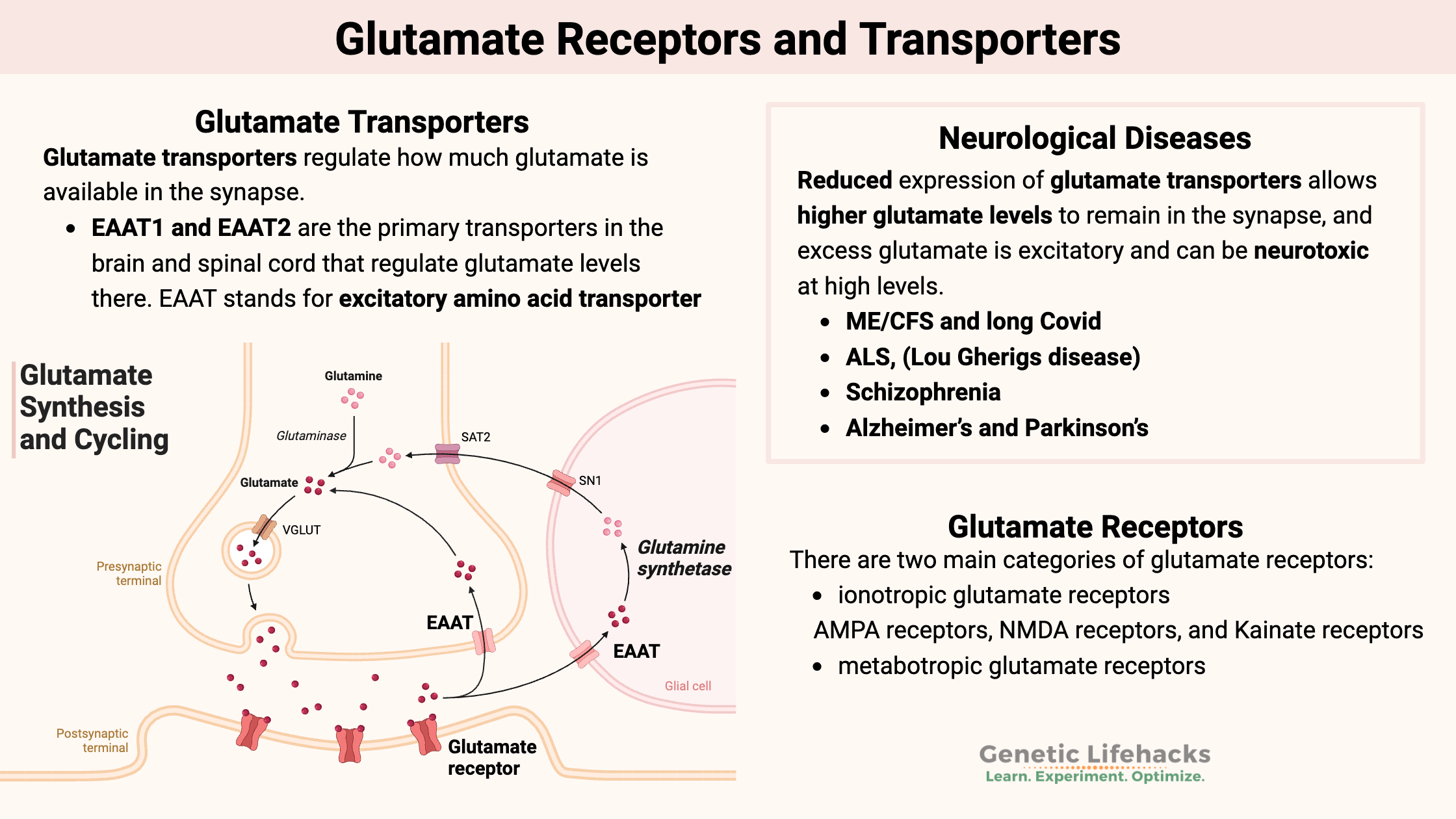
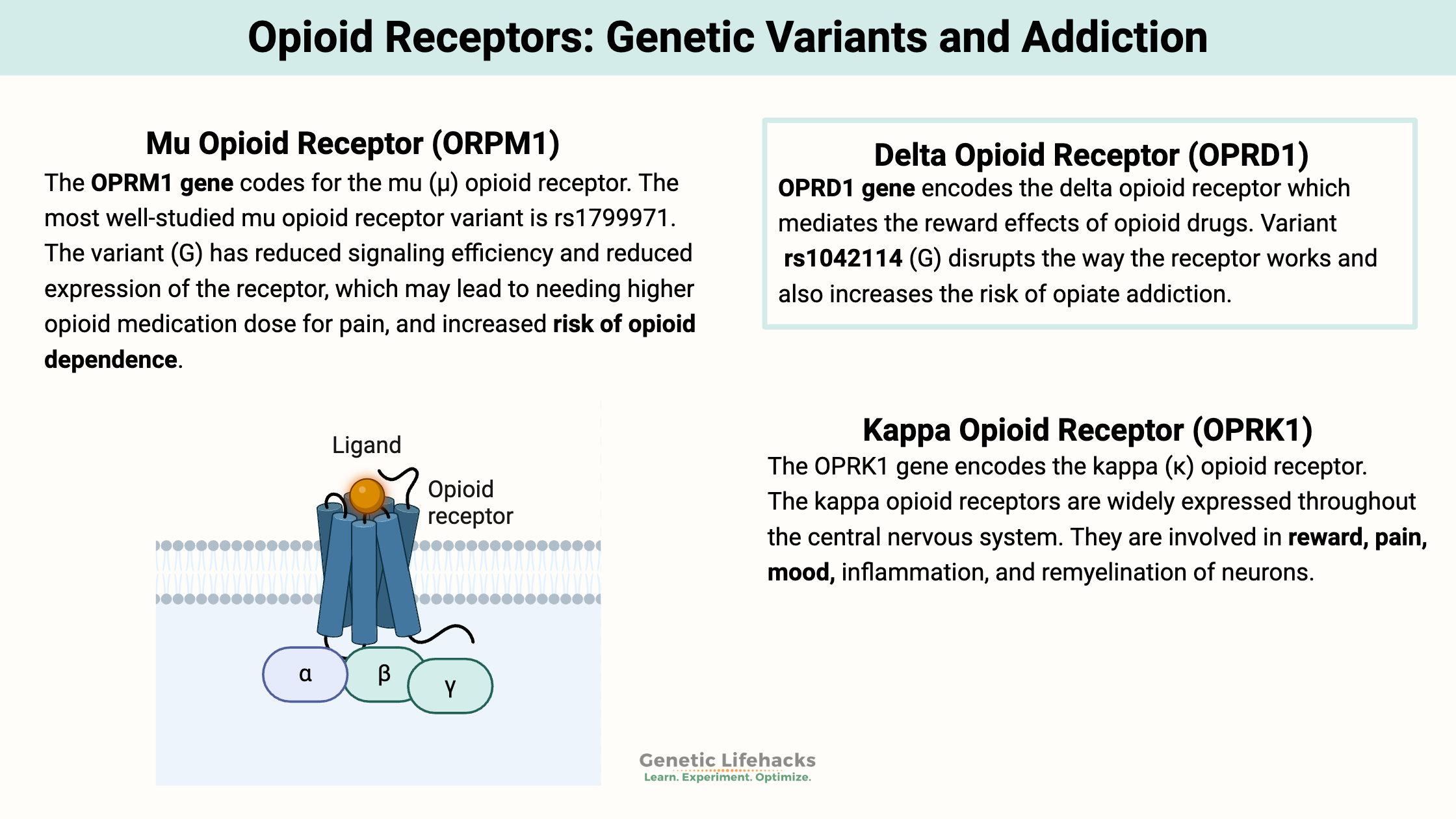
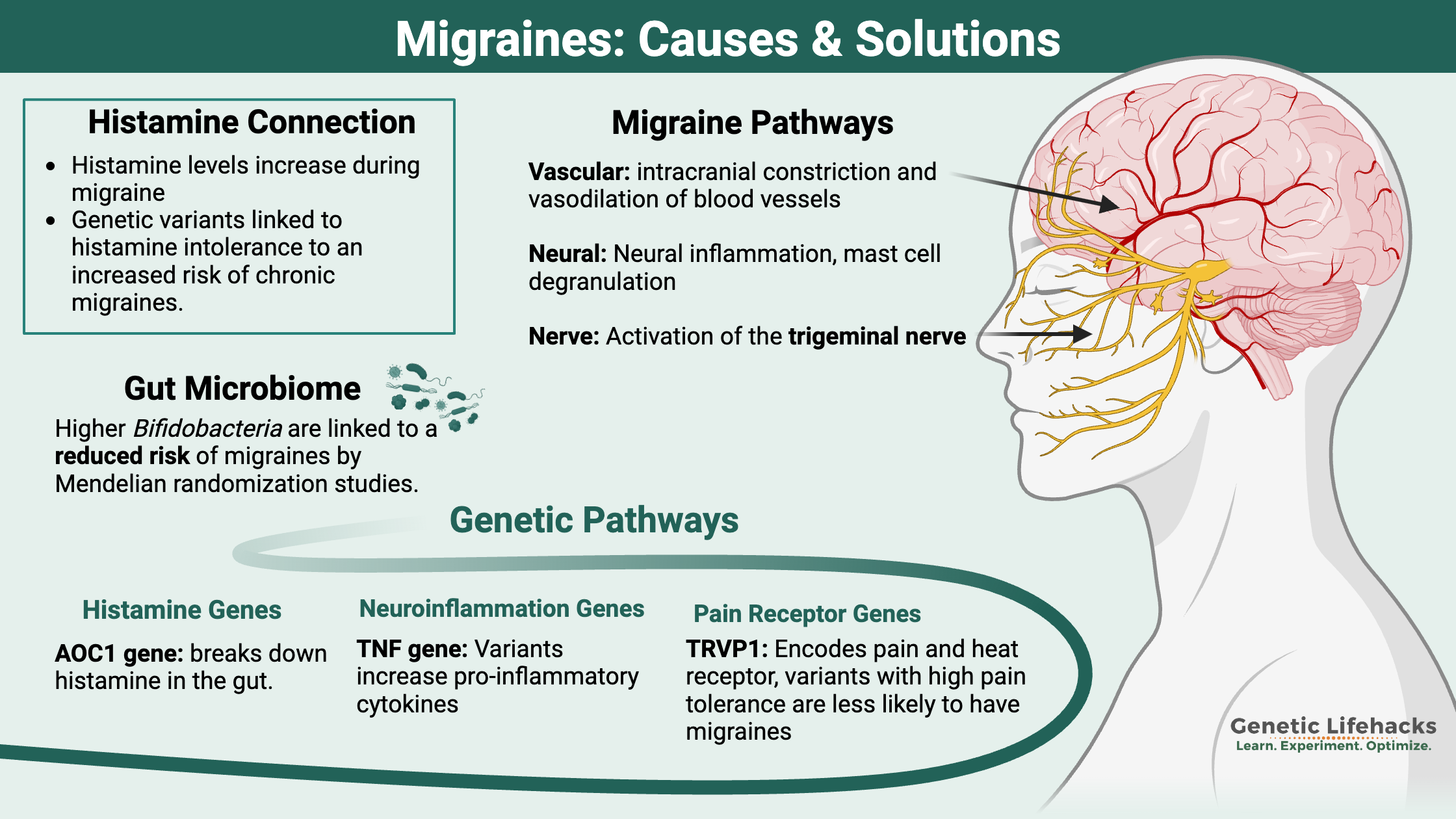
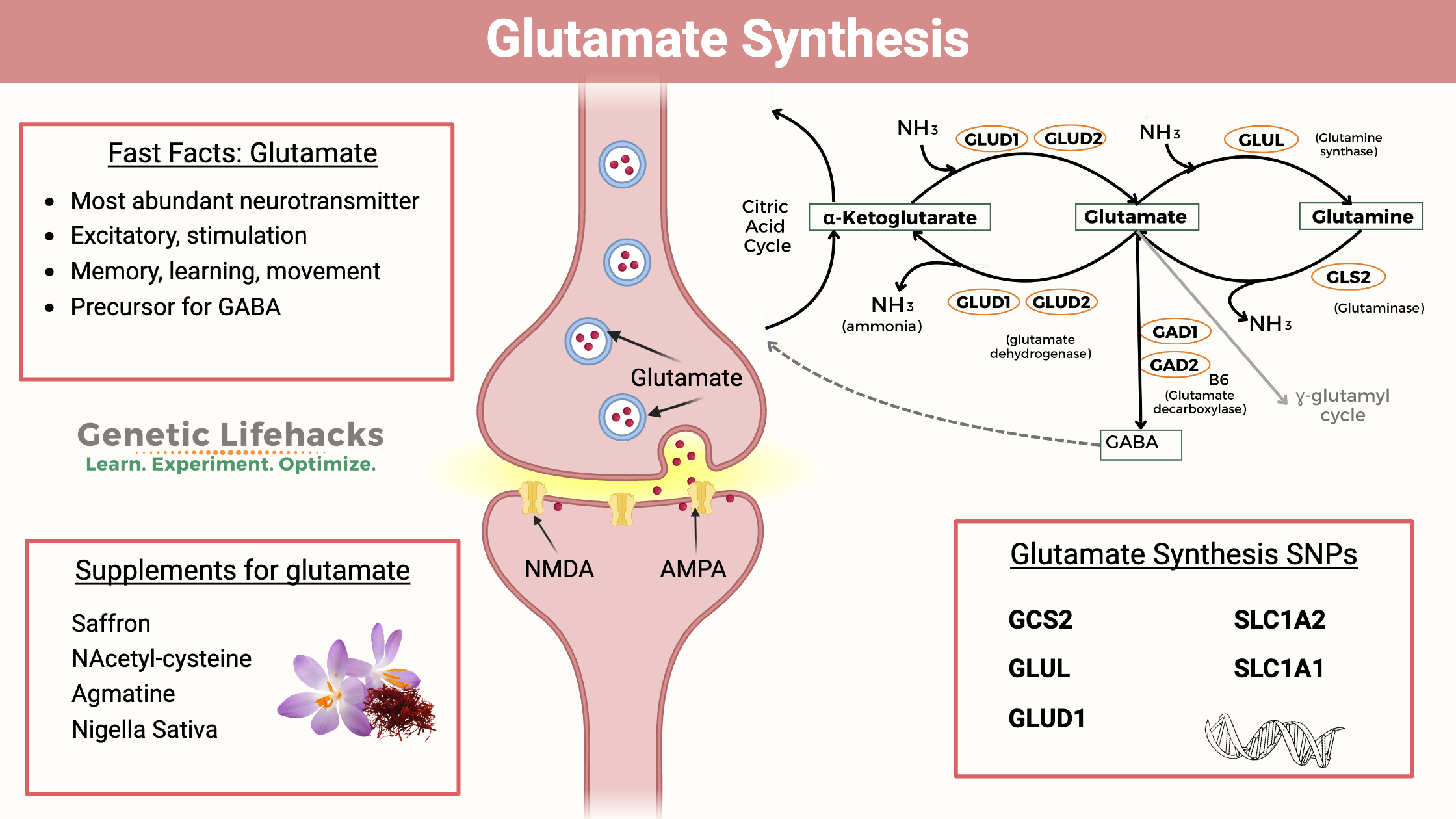
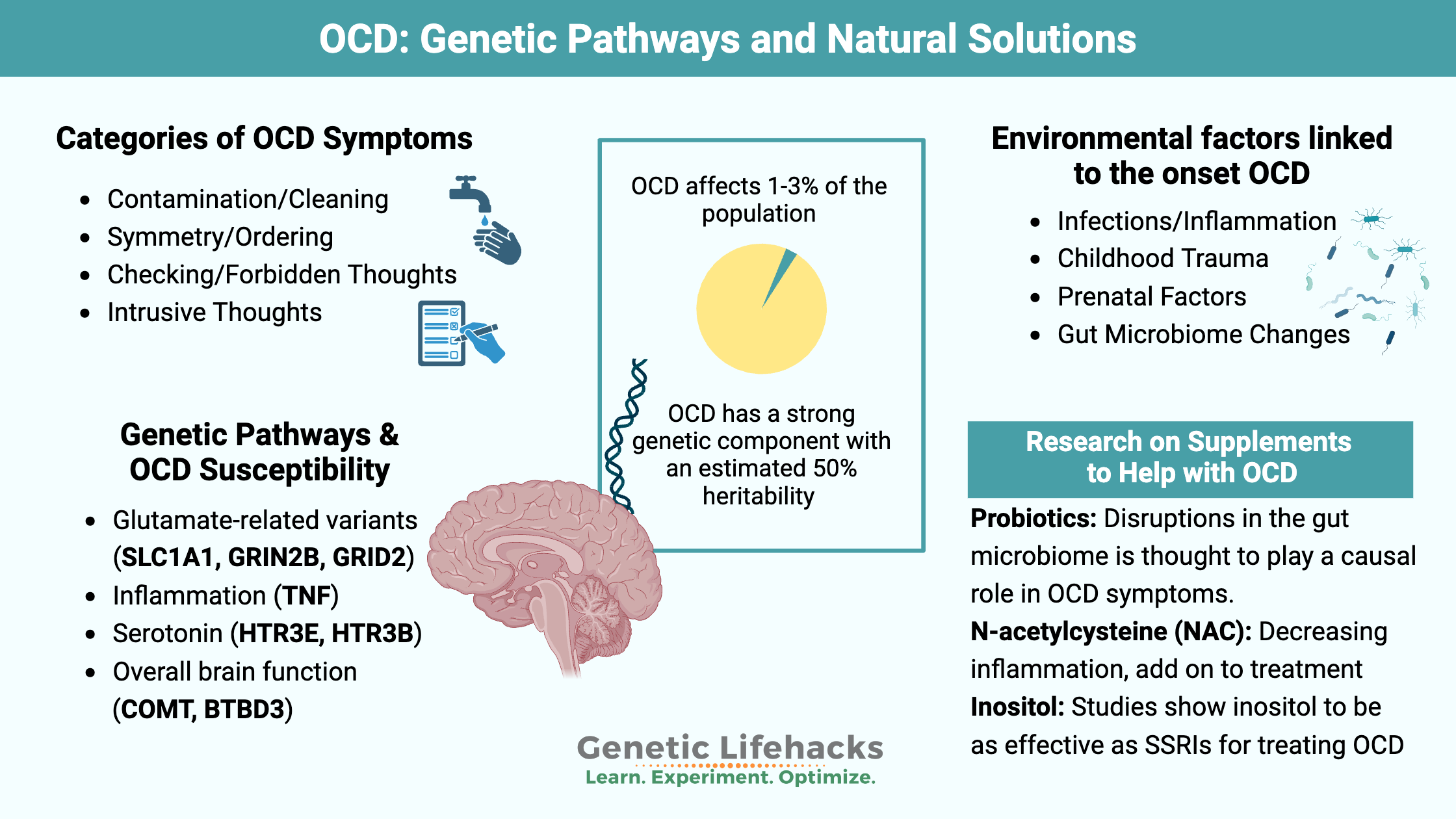
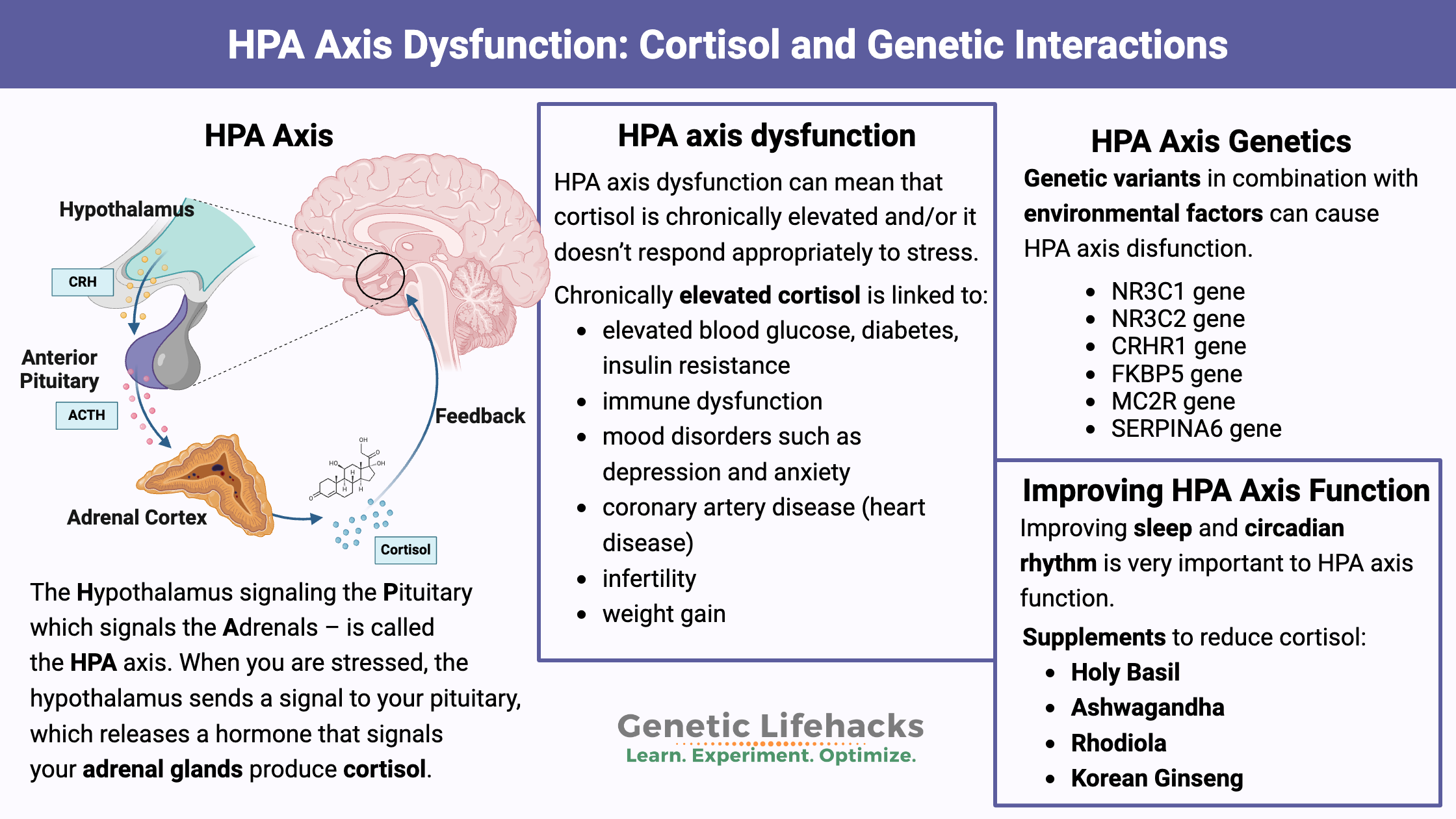
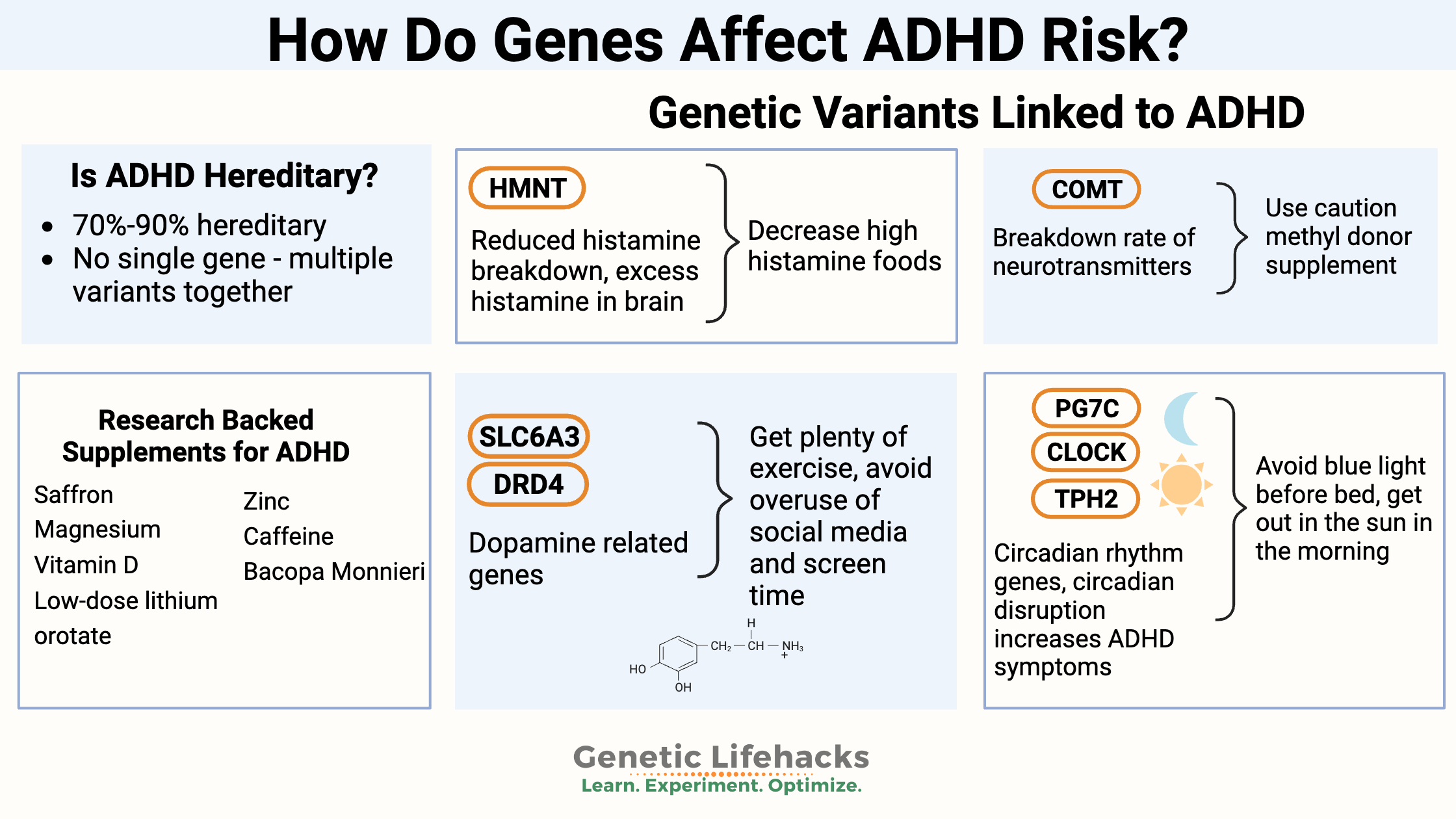
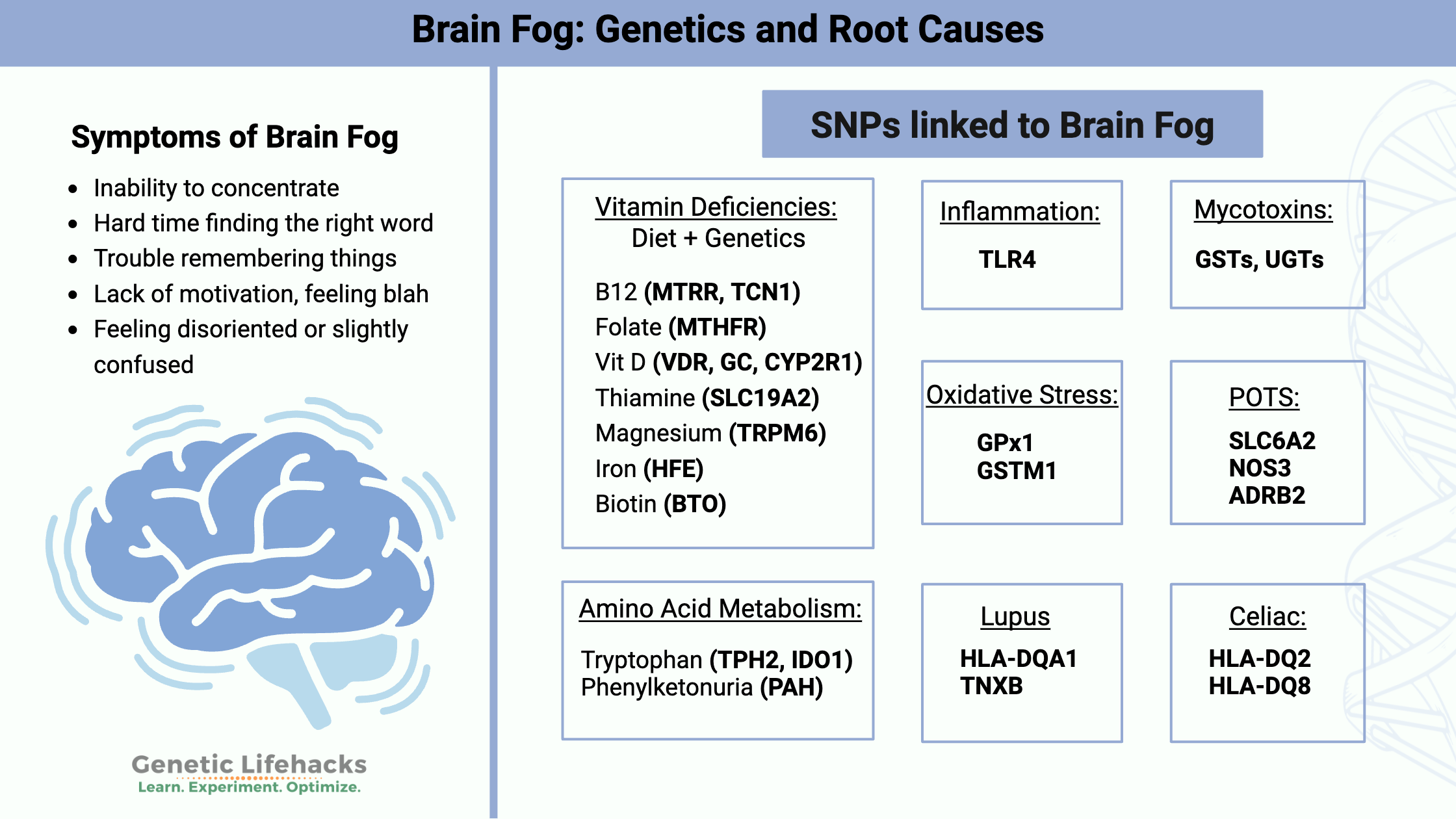
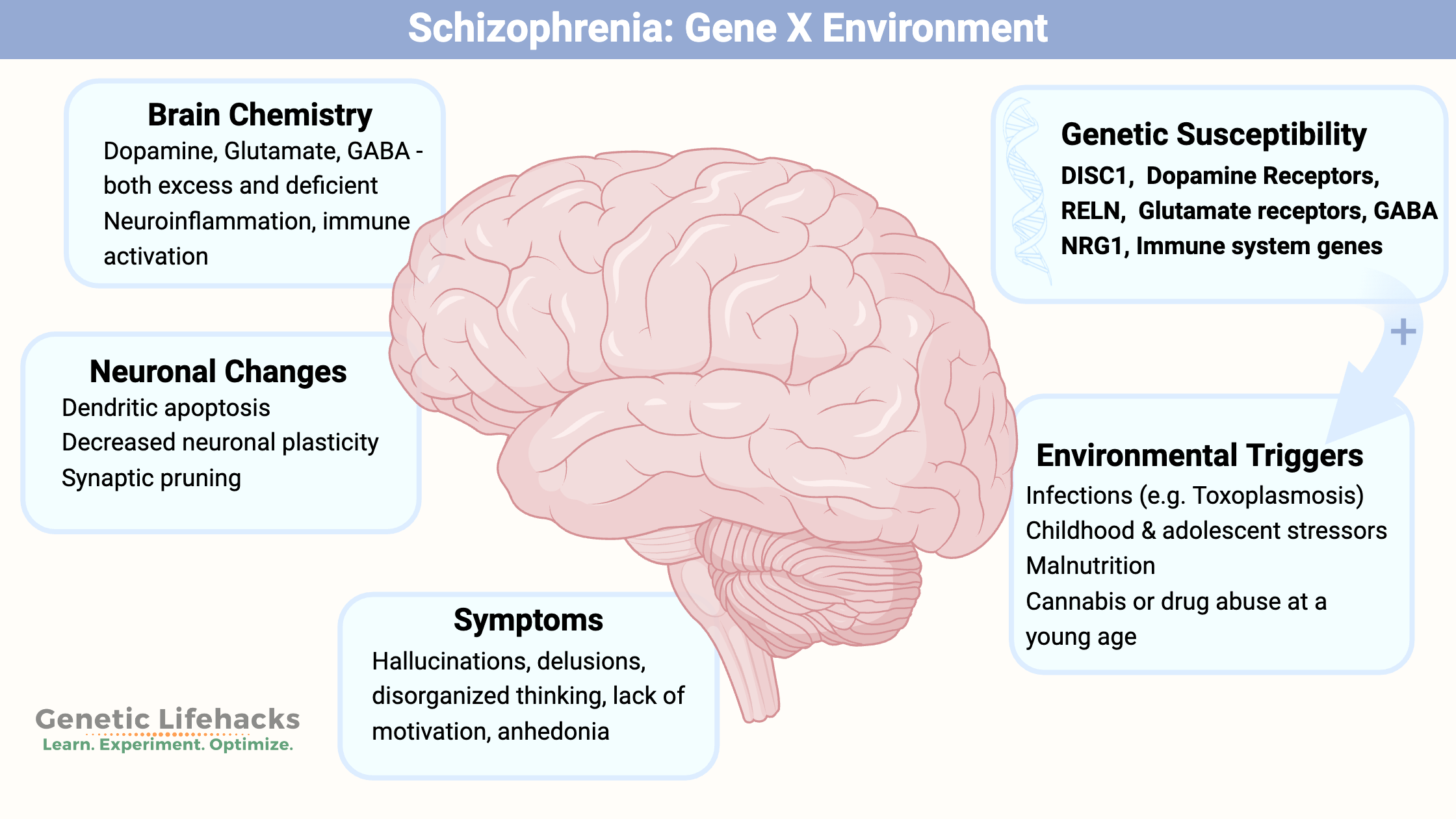
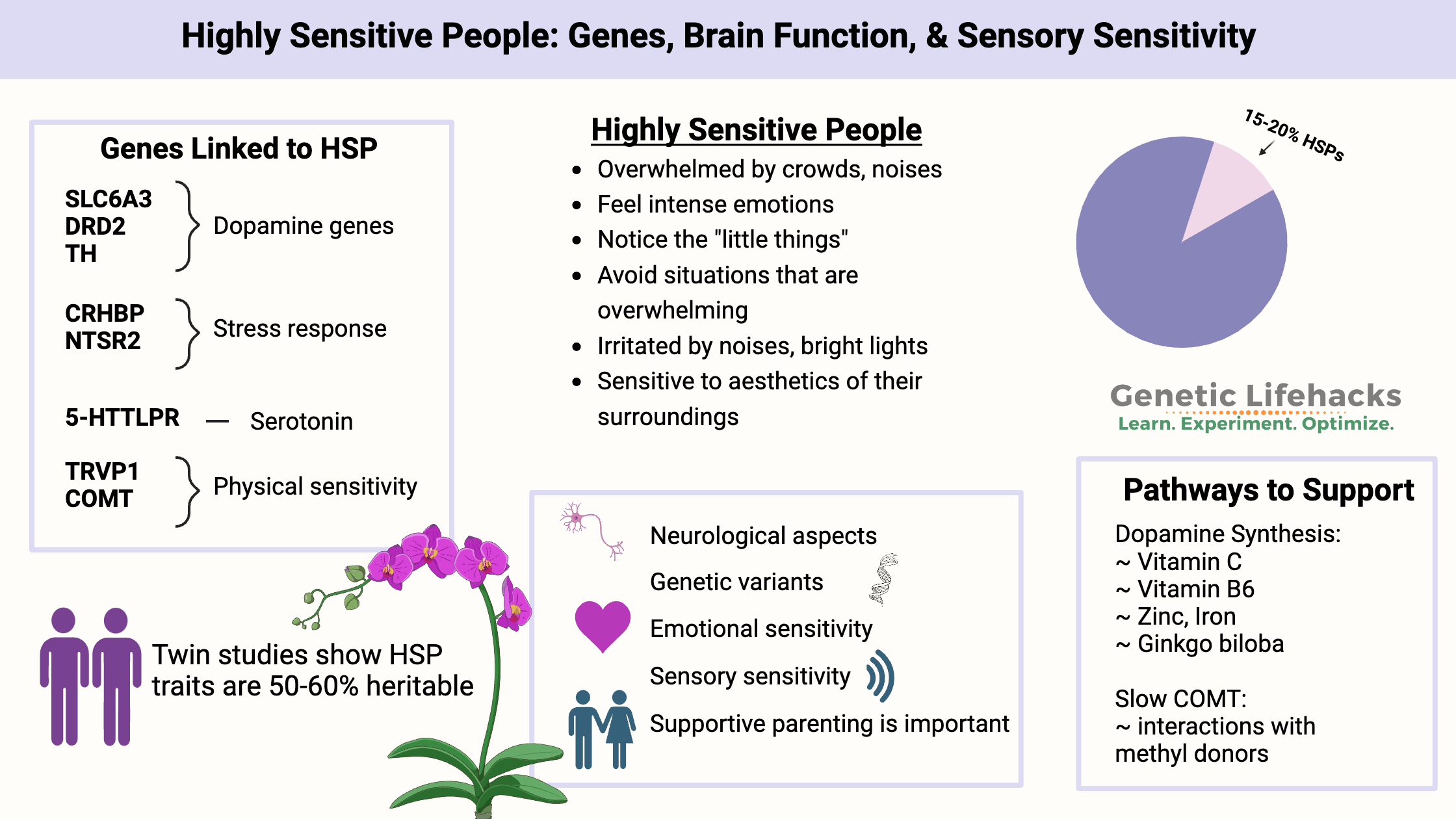
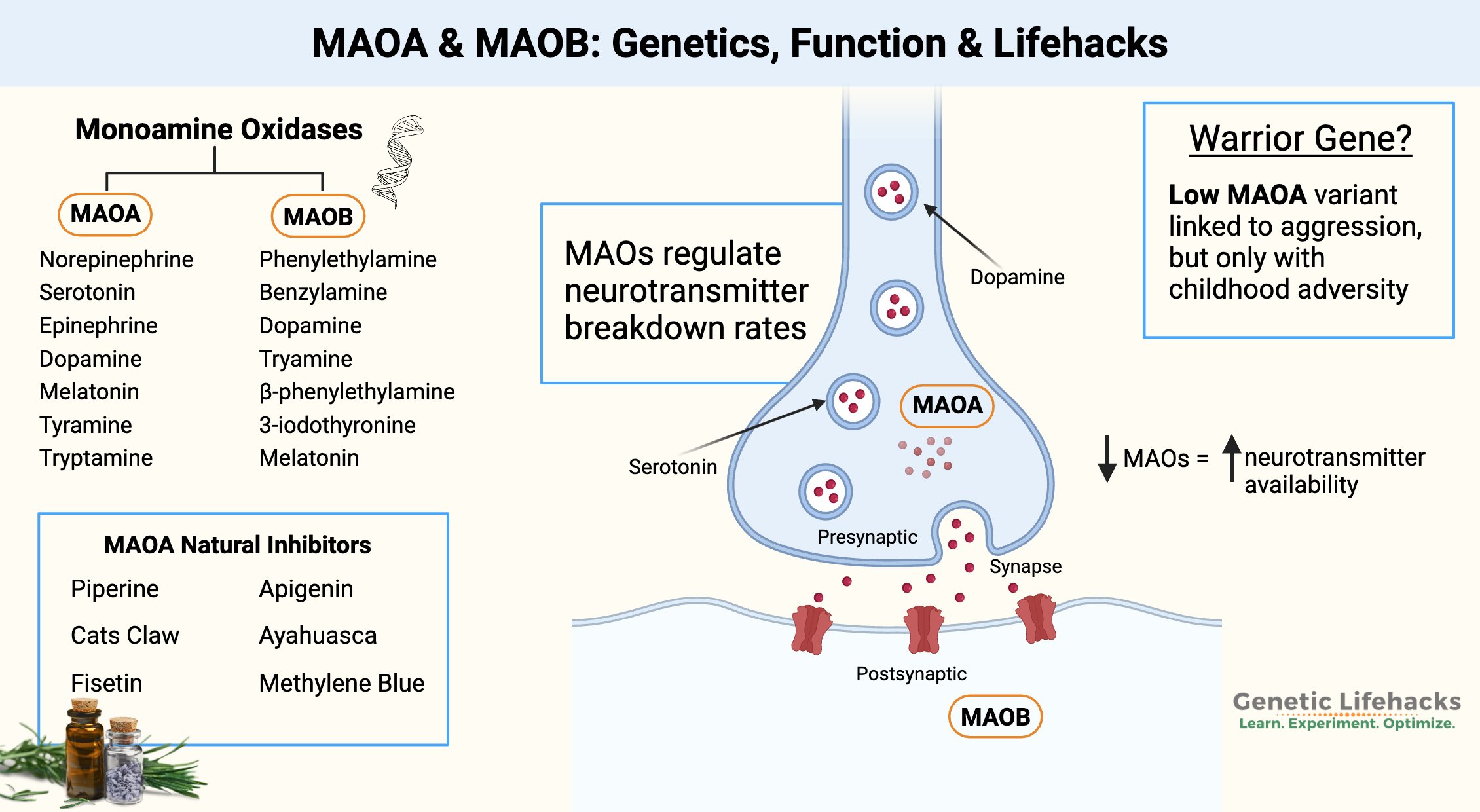
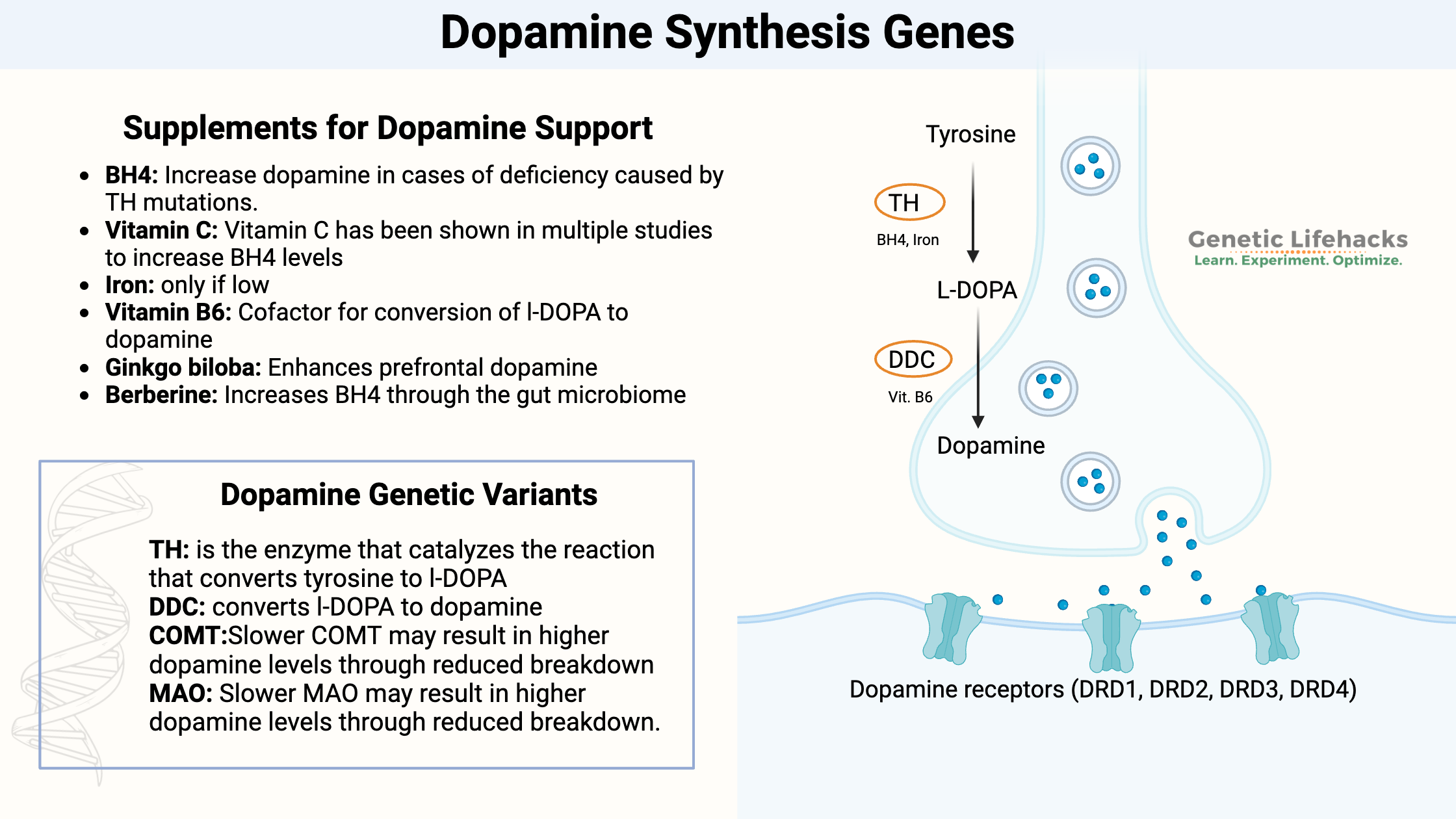
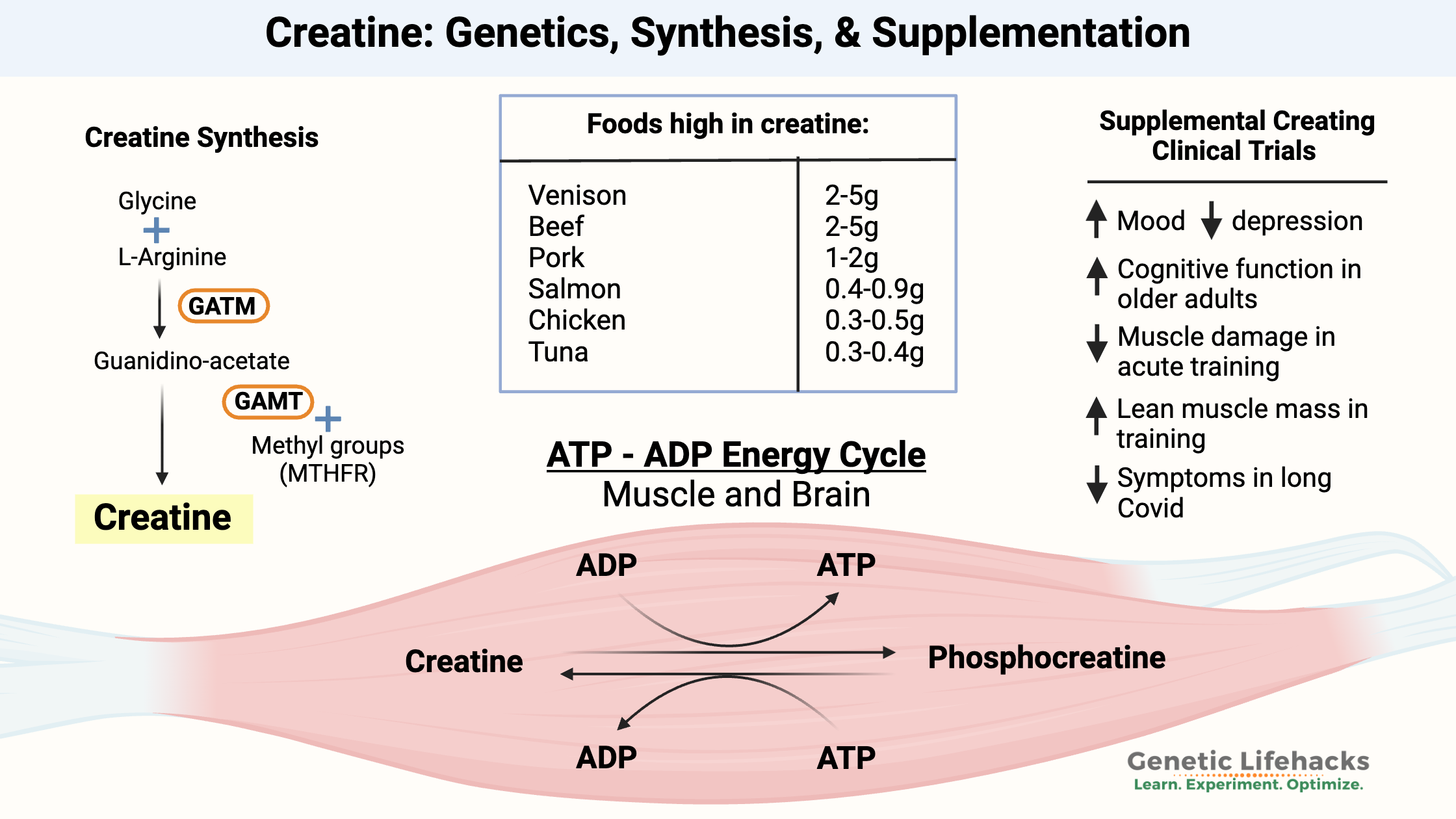
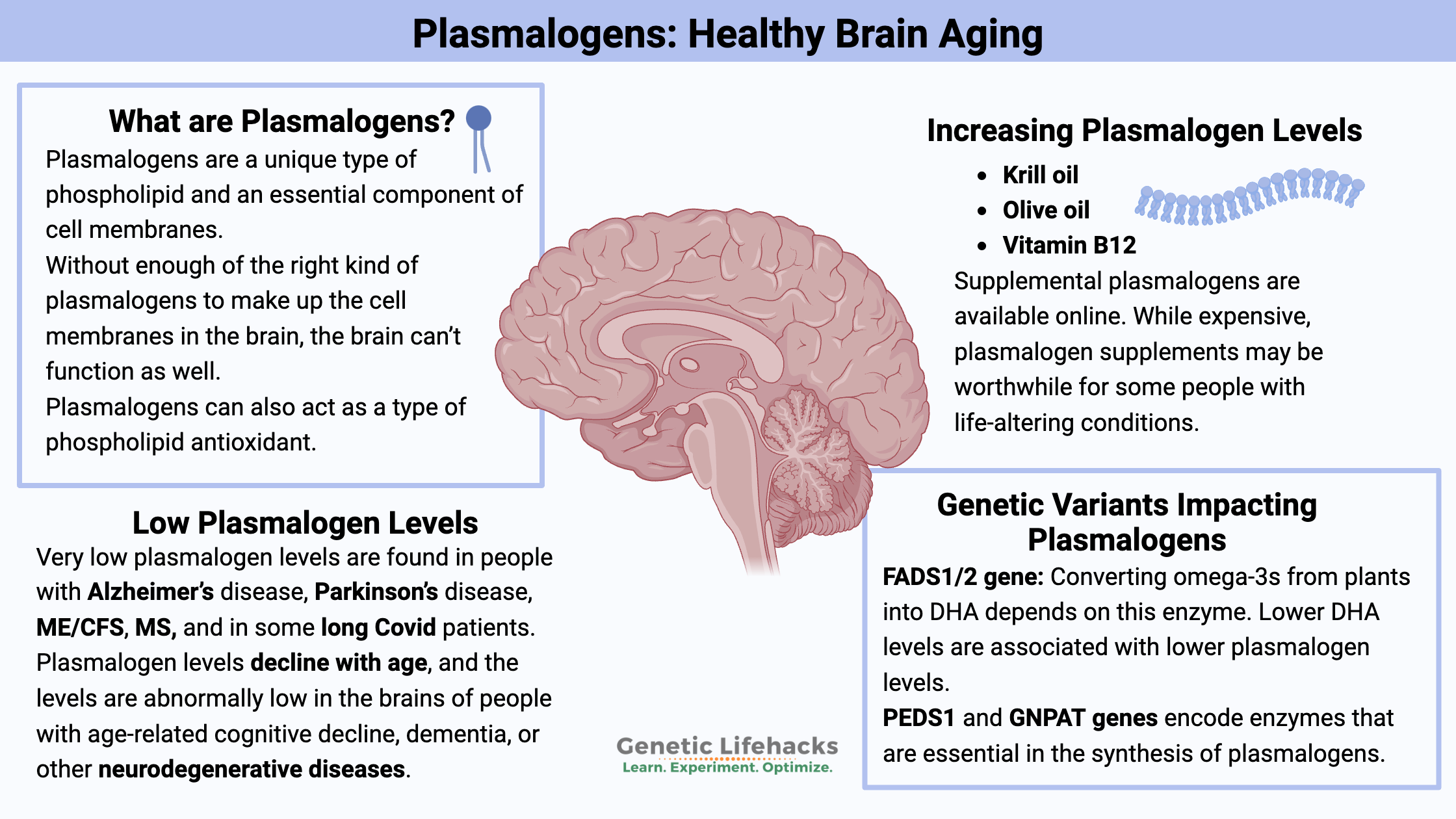
Borderline Personality Disorder: How Genes, Trauma, and Inflammation Interact
Genetics, epigenetics, and childhood trauma all contribute to BPD. Understand the neurotransmitter disruptions, inflammatory markers, and circadian rhythm issues—with solutions that work.