Key takeaways:
~ Sudden deafness – or sudden sensorineural hearing loss – can occur for a number of reasons, including viral infections and vaccinations. Sudden hearing loss usually occurs just in one ear, leading to problems hearing certain ranges of sound.
~ Genetic variants can significantly increase your risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss; knowing the genetic susceptibility leads to understanding why SSNHL occurs.
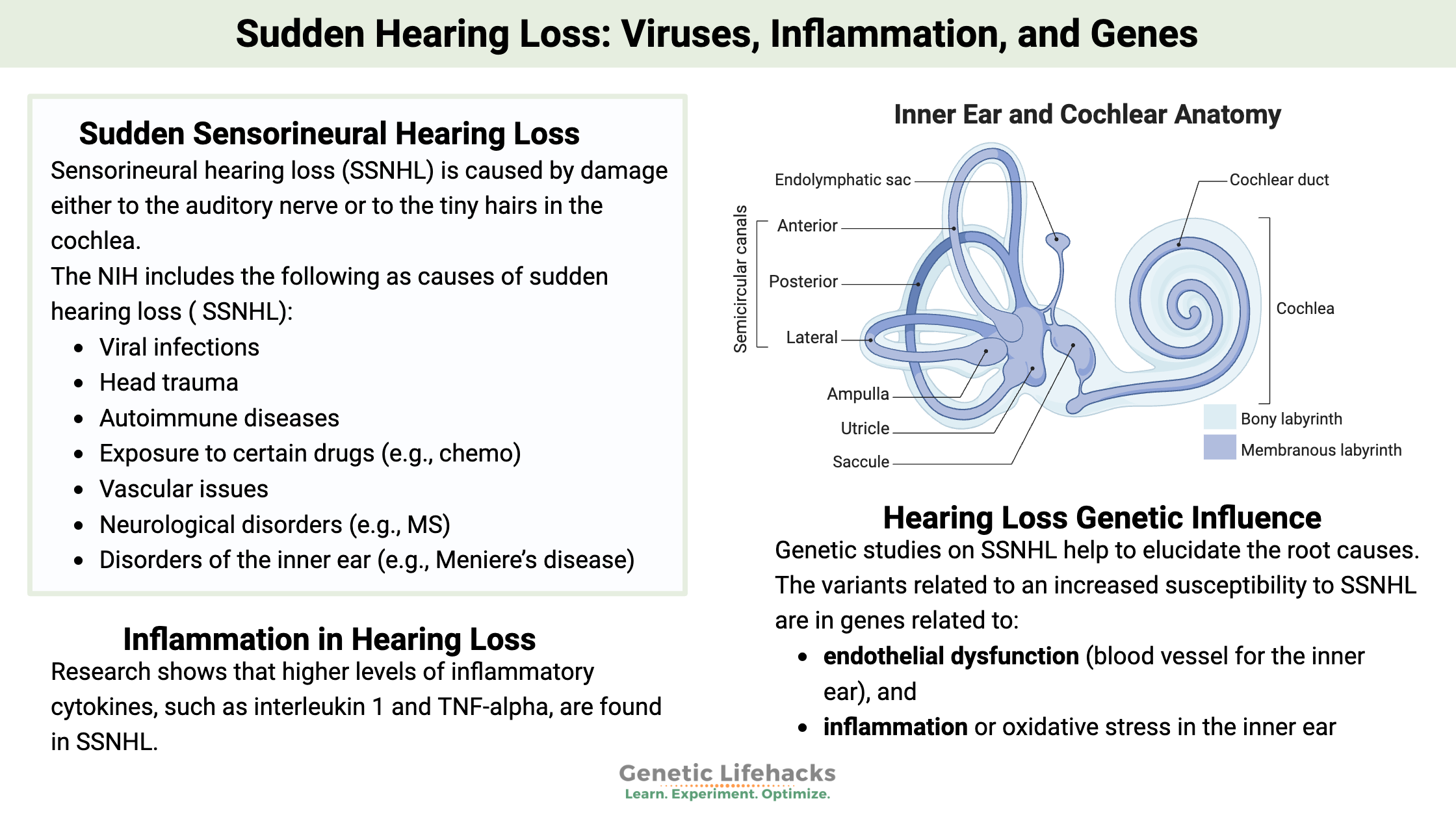
What is sudden sensorineural hearing loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is caused by damage either to the auditory nerve or to the tiny hairs in the cochlea.
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss, also called sudden deafness, is defined as hearing loss “greater than 30 dB in at least three consecutive frequencies that has developed within three days.”[ref] A hearing test can tell you if you’ve lost your hearing at certain frequencies.
It isn’t one of those ‘DIY’ types of health problems. If you think you have sudden hearing loss, head to the doctor because immediate treatment makes it more likely that you’ll recover your hearing.
About 50% of people with sudden sensorineural hearing loss do recover their hearing spontaneously. Usually, hearing recovery happens within a week or two.
The NIH includes the following as causes of sudden hearing loss:[ref]
- Viral infections.
- Head trauma.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Exposure to certain drugs (e.g., chemo)
- Vascular issues
- Neurological disorders (e.g., MS)
- Disorders of the inner ear (e.g., Meniere’s disease).
What is behind SSNHL?
Genetic studies on SSNHL help to elucidate the root causes. The variants related to an increased susceptibility to SSNHL are in genes related to:[ref]
- endothelial dysfunction (blood vessel for the inner ear), and
- inflammation or oxidative stress in the inner ear
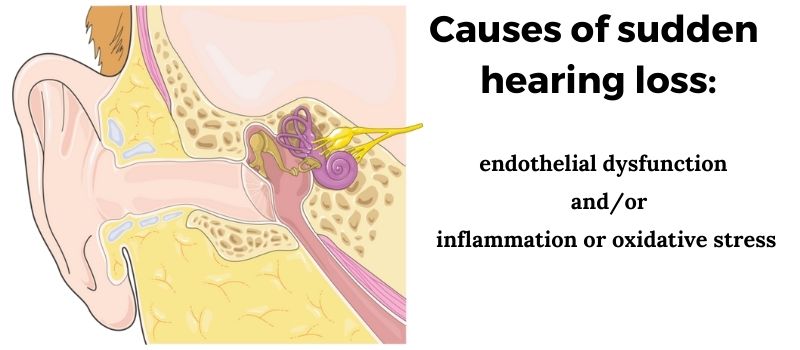
So what suddenly causes inflammation or blood vessel issues? There are several triggers:
Viral infections are a known cause of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. It is thought that epithelial inflammation in the blood vessels supplying the inner ear causes decreased blood flow to this delicate area.[ref]
- Measles and mumps are both long-known causes.[ref]
- Rubella
- Cytomegalovirus[ref]
- Chronic rhinosinusitis[ref] and respiratory infections[ref]
Autoimmune diseases are also a cause of sensorineural hearing loss. Lupus, MS, and rheumatoid arthritis are common autoimmune diseases that increase the risk for SSNHL.[ref][ref]
Chronic diseases that cause vascular problems, such as type 2 diabetes, also increase the risk for SSNHL.[ref]
Sudden, really loud noise exposure can also lead to hearing loss. For example, exposure to sounds over 85 decibels can, over time, lead to hearing loss. Sudden exposure to really loud noise (like an explosion) can lead to sudden sensorineural hearing loss.
Chemotherapy drugs can also cause SSNHL due to high oxidative stress in the hair cells in the ears.[ref]
Vaccinations are also linked to SSNHL. Let’s dive into this further…
Vaccines and sudden hearing loss:
A report using data from the VAERS database from 1990 until 2003 showed that the live attenuated vaccines for measles and mumps were associated with 44 likely cases of hearing loss after immunization.[ref] Keep in mind that this study covered more than a decade of data, and the event rate was estimated to be 1 case per 6-8 million doses.
A case study reported sudden deafness after a rabies vaccine.[ref]
Several case studies and research studies have been published on sudden sensorineural hearing loss after COVID-19 vaccination. In fact, a 2022 report that adds together the published case studies shows about 1,200 case reports that physicians have written up. It does not include the 2000+ reports in VAERS.[ref][ref][ref
Inflammation in hearing loss:
I mentioned above that vascular dysfunction can cause hearing loss. It makes sense – when blood can’t reach the delicate depths of the ear, then the delicate parts of the inner ear can’t function properly.
The other causal factor in SSNHL is inflammation. Research shows that higher levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin 1 and TNF-alpha, are found in SSNHL. Inflammation ties into vascular dysfunction also, because it can cause swelling and vascular spasms.[ref]
Many of the genetic variants that researchers have identified for sudden hearing loss are in genes related to inflammation. For some people, genetic variants increase the inflammatory response – great for fighting off certain pathogens, but often a problem when overly active.
The two most common causes of SSNHL are autoimmune diseases or infections (viruses, syphilis). Both can cause a sudden increase in inflammation. The standard treatment for sudden hearing loss is corticosteroids, which reduce inflammation.[ref]
Heat shock proteins:
Heat shock proteins are activated by cells in response to a stressful condition, such as exposure to high heat. Heat shock proteins act as ‘chaperones’, a cell biology term meaning that they help stabilize or ensure the correct folding of other proteins under stress conditions. These resilience champions come alongside and help the other proteins needed in cellular function.
Elevated levels of heat shock protein 70 are found in people with SSNHL. Genetic variants related to heat shock protein 70 are related to hearing loss (sudden or age-related).[ref][ref]
Resolving inflammation: An active process
The process of resolving inflammation is an active one, with anti-inflammatory molecules, such as resolvin, lipoxin, and maresin, being produced to actively resolve the inflammation. Pro-resolving mediators not only shut off the pro-inflammatory response but also play a critical role in clearing inflammatory waste products and restoring homeostasis. This is true for inflammatory processes throughout the body, such as heart disease, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis… and hearing loss.[ref]
Researchers are now working to understand how to package and deliver pro-resolving mediators as a drug for curing SSNHL.[ref]
Sudden Hearing Loss Genotype Report:
Genetic variants are linked to an increased relative risk of sudden hearing loss.
Let me give you an example to put this in perspective: If the normal risk of SSHL is 1 in 5,000, a variant that triples the risk puts your risk at 3 in 5,000. The genetic risk factors, though, give us a view into the role of infections, inflammation, and immune response. Not all variants associated with SSHL are included in 23andMe or AncestryDNA data.[ref]
Understanding where your genetic susceptibility lies may help you find the best treatment for you.
Access this content:
An active subscription is required to access this content.
Lifehacks:
It is definitely a situation where you should seek high-quality medical help from a specialist as quickly as possible. Time is of the essence in treating SSNHL, and earlier treatment is associated with a greater chance of getting your hearing back.
Below are research-based solutions that you can discuss with your hearing specialist.
Reduce inflammation: Corticoid steroids to reduce inflammation in the inner ear are usually the first line of treatment.[ref] This is why it is important to talk with your doctor as soon as you can.
Steroids plus vitamin D: A clinical trial in China looked at the addition of vitamin D to the standard of care for sensorineural hearing loss. Both groups received conventional therapy of methylprednisolone and ginkgo biloba extract. The participants who also received vitamin D3 had significantly greater improvement for hearing restoration and for reducing tinnitus. [ref]
Early hyperbaric oxygen therapy: A case study showed that the combination of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (along with the standard treatment of high-dose corticosteroids) was effective for the full recovery of hearing. The patient was treated with 15 daily 1-hour exposures to 100% oxygen at 1.5 atmospheres absolute, along with the corticosteroids.[ref] Multiple clinical trials also point to hyperbaric oxygen therapy along with corticosteroids as being statistically more effective than steroids alone.[ref][ref]
Dexamethasone in the ear: While systemic steroids are usually the first option for sensorineural hearing loss, another treatment option to talk with your hearing specialist about is intratympanic dexamethasone (injection of the steroid into the ear).[ref] A retrospective study found that intratympanic dexamethasone improved hearing in 40% of patients compared to only 13% in the control group of systemic steroids.[ref][ref]
Supplement Research:
Access this content:
An active subscription is required to access this content.
Related Articles and Topics:
MTR and MTRR Genes: Vitamin B12, Homocysteine, and Methylation