Understanding your genetic variants (SNPs), along with clinical trials and quality research studies, can help you narrow down the natural supplements that may actually help – versus the supplements that are likely a waste of money. Genes can also come into play with whether you’re likely to have side effects from a supplement.
Please be sure to click through to the full article on each of the supplements. It contains additional information on clinical trials, safety, lab tests on supplement brands, and other considerations.
Always talk to your doctor or pharmacist about supplement interactions with prescription medications or for medical advice.
Jump to: Ashwagandha, Luteolin, Curcumin, Berberine, Quercetin, Hesperidin, Nattokinase, CoQ10, Nicotinamide Riboside, Creatine
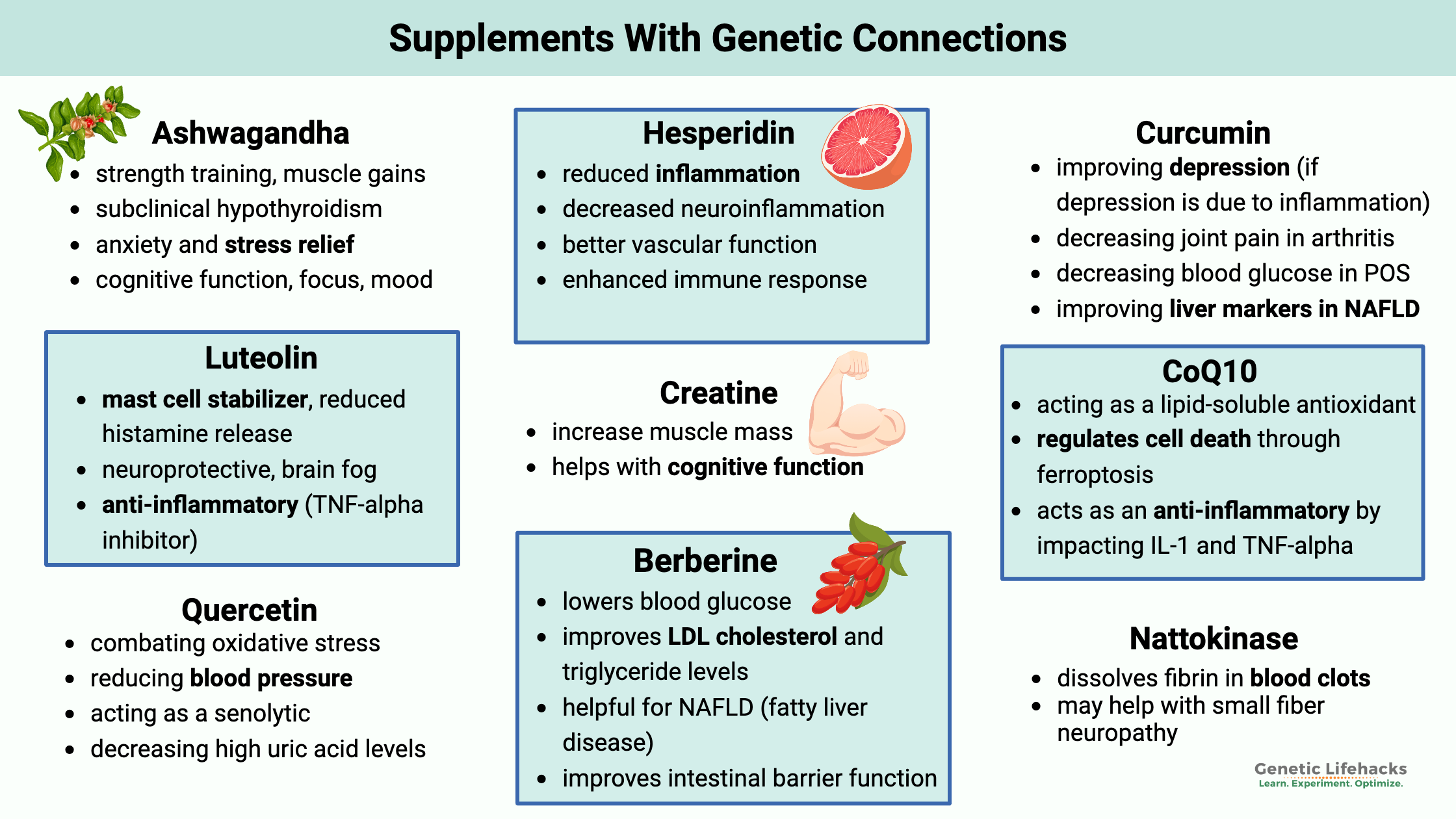
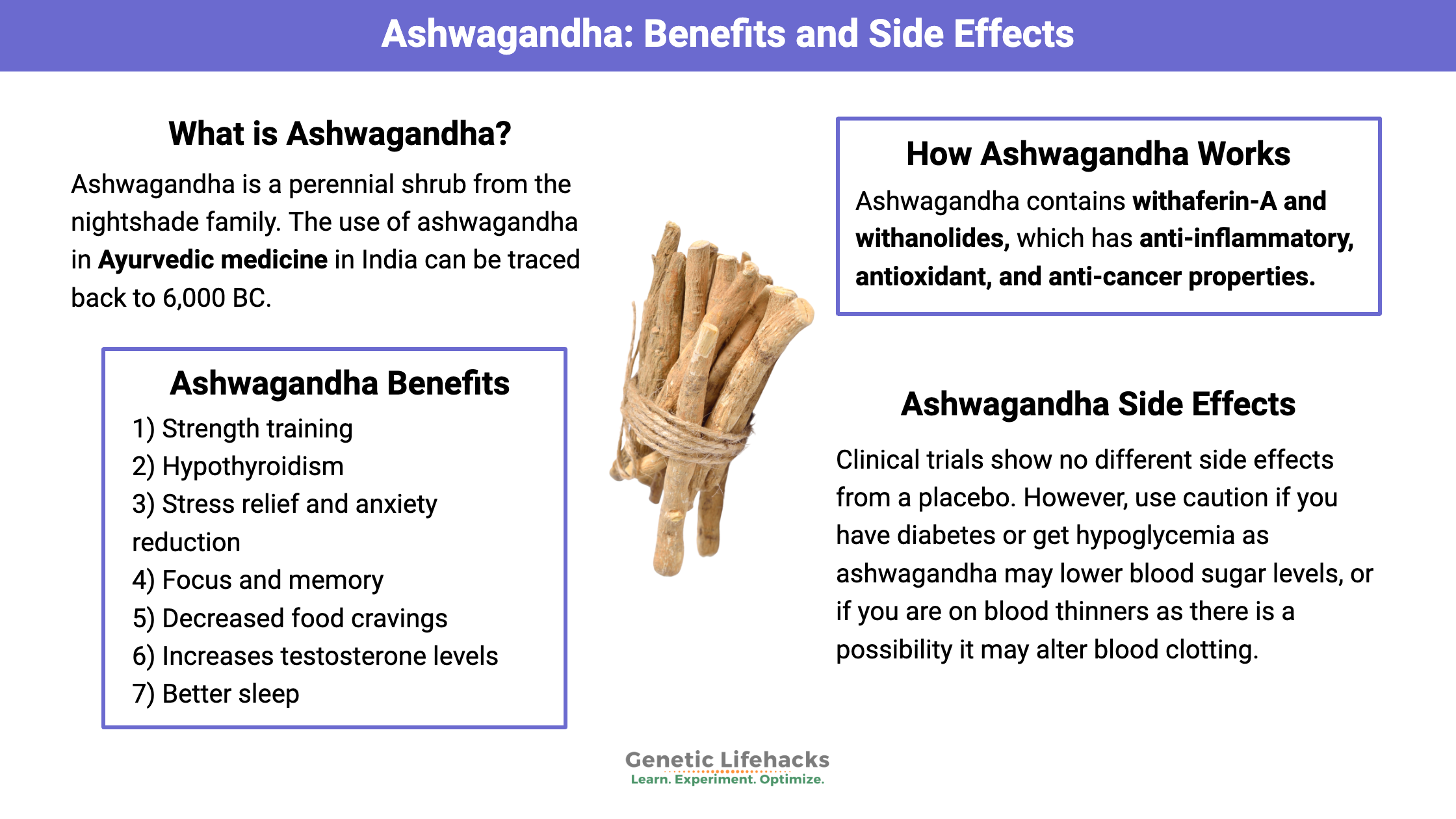
Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is a traditional Ayurvedic herb used for centuries to counter stress and anxiety. Research shows that it has many benefits beyond just mood including:
- strength training, muscle gains
- subclinical hypothyroidism
- anxiety and stress relief
- cognitive function, focus, mood
- decreased food cravings if due to stress
- testosterone
- sleep quality
- sexual function (women)
Get the details on ashwagandha research studies here.
Ashwagandha may work well for:
Cortisol and HPA axis dysfunction:
Research shows ashwagandha effectively regulates cortisol levels in people with HPA axis dysfunction. The full article explains the genetic variants that increase susceptibility to issues with the HPA (hypothalamus – pituitary – adrenal) axis, including altered cortisol rhythm.
Cortisol and HPA Axis genes (Please read the full article for details):
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR3C1 | rs6189 | T | -- | Glucocorticoid receptor mutation linked to cortisol resistance |
| NR3C1 | rs6190 | T | -- | Glucocorticoid receptor mutation linked to cortisol resistance |
| NR3C1 | rs6198 | C | -- | Glucocorticoid receptor mutation linked to cortisol resistance |
| NR3C1 | rs56149945 | C | -- | Increased sensitivity to glucocorticoids;increased risk of obesity; hypertension |
| NR3C1 | rs41423247 | C | -- | Hypersensitivity to glucocorticoids |
| NR3C1 | rs6191 | A | -- | GR variant linked to some resistance to cortisol (minor) |
| NR3C1 | rs10052957 | A | -- | Linked to hypersensitivity to cortisol (minor) |
| NR3C2 | rs5522 | C | -- | Associated with resistance to cortisol; depression. |
| CRHR1 | rs110402 | G | -- | Elevated adult cortisol if exposed to childhood trauma; increased risk of depression or anxiety |
| CRHR1 | rs242924 | G | -- | Elevated adult cortisol if exposed to childhood trauma; increased risk of depression or anxiety |
| CRHR1 | rs242941 | A | -- | Increased risk of depression |
| CRHR1 | rs242939 | C | -- | Increased risk of depression |
| FKBP5 | rs1360780 | T | -- | Incomplete cortisol recovery; risk of depression; anxiety |
| FKBP5 | rs3800373 | C | -- | Incomplete cortisol recovery; risk of depression; anxiety |
| MC2R | rs1941088 | A | -- | low cortisol response |
| MC2R | rs28940892 | C | -- | Mutation linked to ACTH resistance (important) |
| SERPINA6 | rs11621961 | T | -- | Less cortisol binding globulin; lower plasma cortisol |
| SERPINA6 | rs941601 | T | -- | Less cortisol binding globulin; lower plasma cortisol |
| NR3C1 | i4990006 | C | -- | Increased sensitivity to glucocorticoids;increased risk of obesity; hypertension |
Genetics and Anxiety:
Ashwagandha has many studies on it showing that it may help with anxiety if it is due to stress and high cortisol. One study tested 300 mg, 2x a day vs. placebo. After 8 weeks, cortisol was reduced by an average of 22%, which is significant. Weight also went down for the Ashwagandha group.[ref]
Anxiety genes (Please read the full article for details):
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADORA2A | rs5751876 | T | -- | TT: Increased risk panic disorder; Increased anxiety with high caffeine |
| OXTR | rs53576 | A | -- | less empathetic, less sensitive to social rejection (more resilient); G/G: increased separation anxiety risk |
| GNB3 | rs5443 | T | -- | When combined with OXTR rs5443 GG - Increased separation anxiety |
| SLC6A4 | rs140701 | T | -- | Increased risk panic disorder; social anxiety disorder |
| BDNF | rs6265 | T | -- | Decreased BDNF; Increased risk anxiety disorders |
| FKBP5 | rs1360780 | T | -- | TT only: incomplete cortisol recovery; Increased anxiety after psychosocial stress |
| CHCR1 | rs110402 | G | -- | Increased cortisol in childhood trauma |
| ACCN2 | rs10875995 | C | -- | Heightened reactivity to high CO2 levels; Increased risk panic disorders |
| ACCN2 | rs685012 | C | -- | Heightened reactivity to high CO2 levels; Increased risk panic disorders |
Testosterone:
Ashwagandha increases testosterone levels in men who lift weights or do muscle-building exercises. One study used a supplement containing 21 mg of withanolide glycosides/day for eight weeks and showed an average increase in testosterone of about 15%.[ref] In another eight-week placebo-controlled trial of ashwagandha in younger men who were lifting weights, the men taking 300 mg ashwagandha root extract 2x/day increased muscle strength, arm size, and more than tripled testosterone levels.[ref]
Testosterone genes (Please read the full article for details):
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHBG | rs12150660 | G | -- | Lower free testosterone |
| SHBG | rs6258 | T | -- | Lower free testosterone |
| SHBG | rs6259 | A | -- | Higher SHBG levels |
| SHBG | rs1799941 | A | -- | Higher SHBG levels |
| FAM9B | rs5934505 | T | -- | Lower free testosterone |
| LIN28B | rs7759938 | C | -- | Lower free testosterone |
| FSHB | rs10835638 | T | -- | Lower free testosterone |
| SHBG | rs727428 | T | -- | lower SHBG levels, higher DHT levels |
Precautions with Ashwagandha:
BChE and Nightshades:
Ashwagandha is a plant in the nightshade family. People with BChE severe mutations may have problems with nightshades.
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BChE | rs1803274 | T | -- | K-variant; Decreased BChE; possible problems w/ organophosphates and nightshades |
| BChE | rs1799807 | C | -- | A-variant; possibly delayed recovery from succinylcholine (anesthesia) (important) |
| BChE | rs28933389 | A | -- | F1-variant; possibly delayed recovery from succinylcholine (anesthesia) (important) |
| BChE | rs28933390 | A | -- | F2-variant; possibly delayed recovery from succinylcholine (anesthesia) (important) |
| BChE | rs2668207 | C | -- | Minor decrease in BChE levels |
| BChE | rs1126680 | T | -- | Decreased BChE; Increased risk of hyperhidrosis combined with K-variant |
Additional Articles that reference Ashwagandha:
- Leptin: Ashwagandha, an adaptogenic Ayurvedic herb, appears to be a leptin sensitizer.
- Thyroid: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in adults with hypothyroidism found that ashwagandha reduced serum TSH levels.[ref]
- Male infertility: Ashwagandha increases sperm count, volume, and motility.[ref]
- Sleep report: For sleep issues due to stress, ashwagandha may help.[ref][ref]
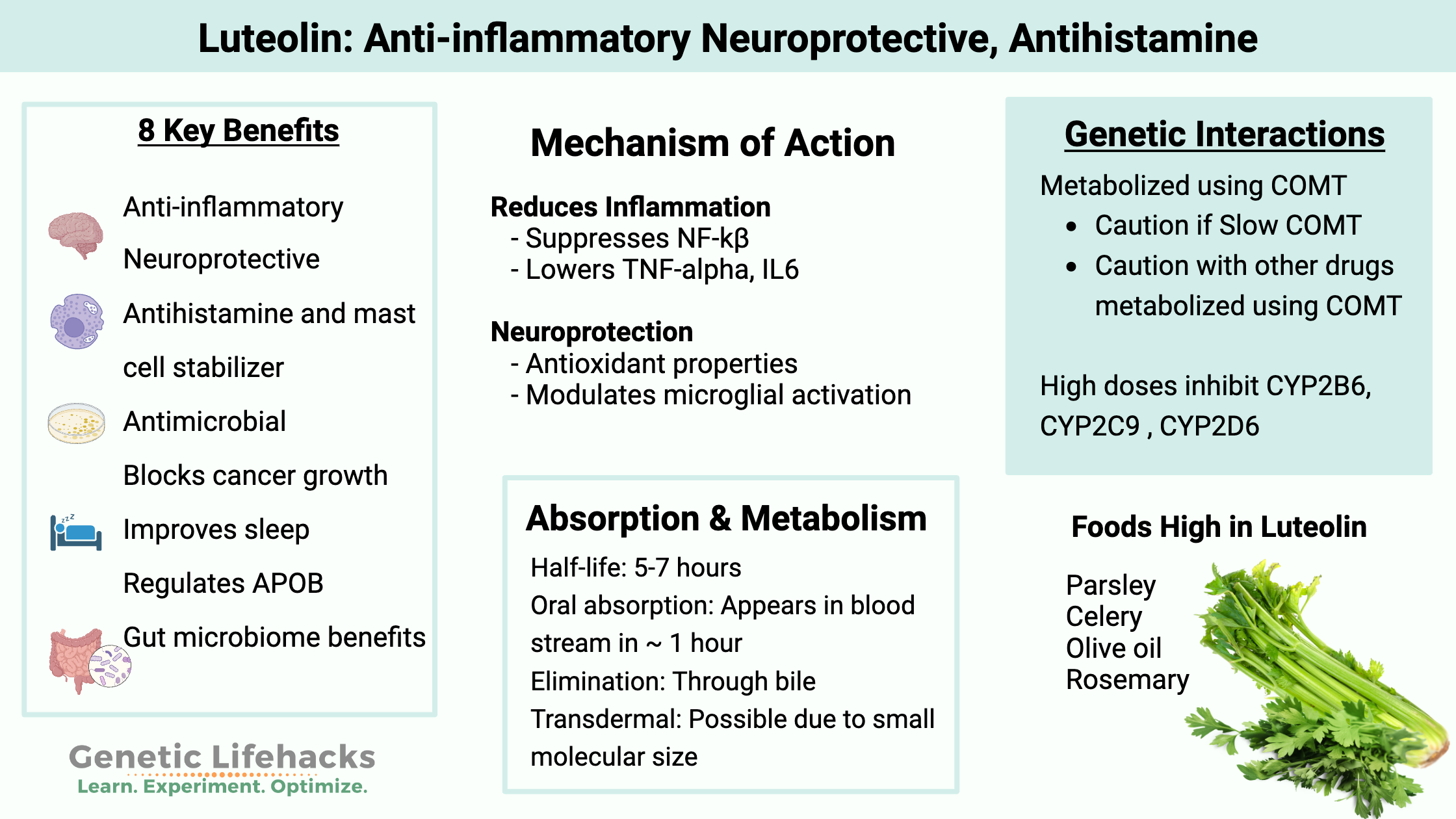
Luteolin
Luteolin is a flavonoid found in abundance in broccoli, parsley, and celery. It possesses a variety of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, according to research. Clinical trials and research on luteolin show:
- mast cell stabilizer; reduced histamine release
- neuroprotective, brain fog
- anti-inflammatory (TNF-alpha inhibitor)
- improves sleep
- anti-microbial
- improving intestinal barrier integrity
Get all the details on luteolin research studies – full article here
Luteolin may work well for:
While there are a lot of reasons for brain fog (see the article), luteolin may be a good option for anyone with inflammation-related cognitive dysfunction. Brain Fog Inflammation genes (Please read the full article for details):
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGA | rs121909612 | A | -- | possibly carrier of a rare mutation related to fibrinogen amyloidosis |
| SERPINF | rs8074026 | T | -- | increase venous clotting risk, reduced breakdown of microclots |
| GPX1 | rs1050450 | A | -- | increased risk of brain fog in Long Covid patients |
| GSTM1 | rs366631 | A | -- | A/A: deletion (null) GSTM1 gene. more common genotype in people with Long Covid brain fog |
| TLR4 | rs10759931 | G | -- | G/G: common genotype, more likely to have poor cognitive outcomes from mild-Covid |
| HFE | rs1800562 | A | -- | C282Y variant, most common cause of hereditary hemochromatosis, iron buildup could cause brain fog |
| HFE | rs1799945 | G | -- | higher iron levels, more of a problem if two copies (GG) or if combined with C282Y |
In a study of children with autism spectrum disorder, luteolin supplementation has significantly decreased TNF levels. The supplement used in the study was NeuroProtek.[ref]TNF genes (Please read the full article for details):
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF | rs1800629 | A | -- | Increased TNF alpha, increased risk of many chronic inflammatory diseases |
| TNF | rs361525 | A | -- | Increased TNF alpha, increased risk of many chronic inflammatory diseases |
| TNF | rs1799964 | C | -- | Increased TNF alpha, increased risk of many chronic inflammatory diseases |
| TNF | rs1799724 | T | -- | Increased TNF alpha, increased risk of many chronic inflammatory diseases |
| TNFRSF1A | rs1800693 | C | -- | Increased risk of multiple sclerosis; increased NF-kB signaling |
| TNFRSF1A | rs767455 | C | -- | Increased risk of inflammatory diseases. |
| TNFRSF1B | rs1061622 | G | -- | Increased risk of psoriasis, lupus |
| TNF | rs1800610 | A | -- | Lower TNF; less inflammation but more susceptible to infectious diseases |
Studies have shown Luteolin to inhibit histamine release from mast cells.[ref]Histamine intolerance genes (Please read the full article for details):
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOC1 | rs10156191 | T | -- | Reduced production of DAO |
| AOC1 | rs2052129 | T | -- | Reduced production of DAO |
| AOC1 | rs1049742 | T | -- | Reduced production of DAO |
| AOC1 | rs1049793 | G | -- | Reduced production of DAO |
| AOC1 | rs2071514 | A | -- | possibly slightly higher DAO |
| HMNT | rs1050891 | A | -- | Reduced breakdown of serum histamine |
| HMNT | i3000469 | T | -- | Reduced breakdown of serum histamine |
| HMNT | rs2071048 | T | -- | T/T: Reduced breakdown of serum histamine (common) |
| HMNT | rs11558538 | T | -- | Reduced breakdown of serum histamine |
| HDC | rs2073440 | G | -- | Decreased histamine production |
| HDC | rs267606861 | A | -- | rare pathogenic mutation, linked to Tourettes |
| HRH1 | rs901865 | T | -- | Increased H1 receptor, increased asthma risk |
| HRH2 | rs2067474 | A | -- | Decreased H2 receptor |
| HRH4 | rs11662595 | G | -- | decreased HRH4 activation (receptor dysfunction), increased risk of progression in non-small cell lung cancer |
| MTHFR | rs1801133 | A | -- | MTHFR C677T, decreased enzyme function, affects methylation cycle |
| MTHFR | rs1801131 | G | -- | MTHFR A1298C, slightly decreased enzyme function, slightly affects methylation cycle |
Precautions with Luteolin:
COMT interaction:
Luteolin is metabolized using the COMT enzyme, so individuals with slow COMT may want to use with caution and watch for mood changes. This may be more important if taking more than one supplement that utilizes COMT (or at high doses).
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMT | rs4680 | A | -- | GG = higher activity; AG=Intermediate activity AA = lower activity |
| COMT | rs4633 | T | -- | CC = higher activity ; TT = lower COMT activity |
| COMT | rs6267 | T | -- | Minor decrease in COMT |
| COMT | rs165599 | A | -- | Minor decrease in COMT |
| COMT | rs165774 | A | -- | lower COMT activity; more likely to have irrational beliefs if subjected to maltreatment in childhood |
More articles that reference luteolin:
- Long Covid:
A researcher theorizes that supplemental luteolin or quercetin can block the inflammasome production initiated by activating the toll-like receptors. The researcher notes that luteolin is a natural flavonoid considered ‘neuroprotective’ and has been shown to reduce brain fog. The researcher suggests combining luteolin, quercetin, and olive oil (for absorption and additional antiviral properties).[ref] - NAFLD (fatty liver): Luteolin protects against fatty liver by improving intestinal barrier integrity. It also increases microbial diversity in the gut, according to animal studies.[ref]
- Chronic Lyme: A study looked at baicalein and luteolin, combined with either iodine or rosmarinic acid, and found that they may be effective against the typical spirochaete form and persistent forms as well.[ref]
- Autophagy: Luteolin seems to activate autophagy after a traumatic brain injury (TBI).[ref]
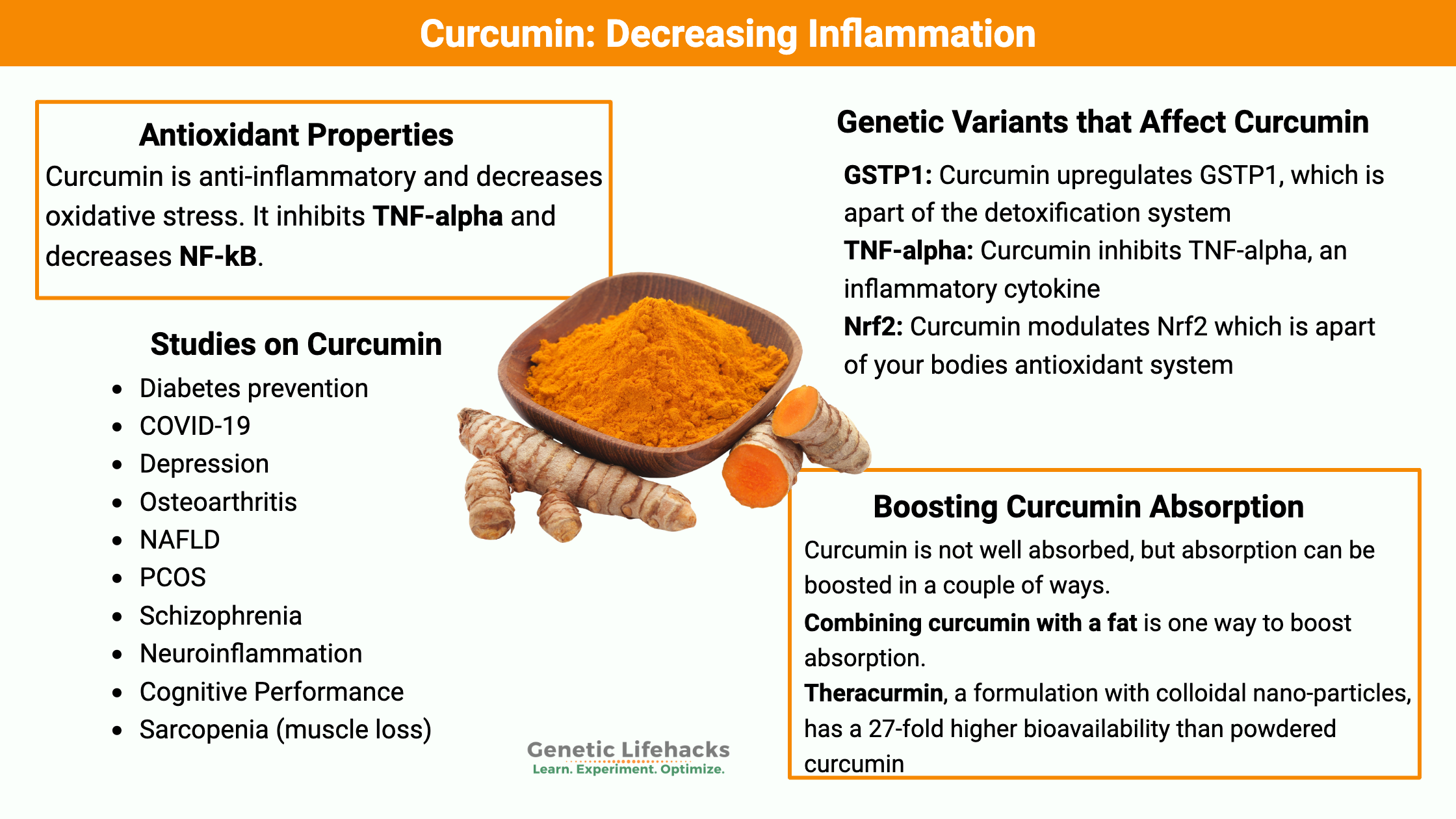
Curcumin
Curcumin, a polyphenol found in turmeric, is a spice used in traditional Indian cuisine and other areas of Asia. It has a long history of use as a spice and in traditional Ayurvedic medicine. Research on curcumin shows that it is anti-inflammatory and decreases oxidative stress. Additionally, research studies show benefits for:
- preventing progression to diabetes from prediabetes
- improving depression (if depression is due to inflammation)
- decreasing joint pain in arthritis
- decreasing blood glucose in POS
- improving liver markers in NAFLD
- helping cognitive function in middle age
Get the full details on curcumin here.
Curcumin may work well for:
Curcumin increases the UGT enzymes and upregulates the glucuronidation pathway, essential for mycotoxin elimination.[ref]
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XPC | rs2228001 | G | -- | Increased relative risk of liver cancer with aflatoxin B1 exposure |
| CYP1A2 | rs12720461 | T | -- | Decreased CYP1A2 enzyme activity, which may impact detoxification of aflatoxin B1 |
| CYP1A2 | rs72547517 | A | -- | Decreased CYP1A2 enzyme activity, which may impact detoxification of aflatoxin B1 |
| CYP1A2 | rs72547515 | A | -- | Decreased CYP1A2 enzyme activity, which may impact detoxification of aflatoxin B1 |
| CYP3A4 | rs4987161 | G | -- | CYP3A4*17, decreased function of enzyme; involved in phase I detoxification of aflatoxin G1 |
| CYP3A4 | rs4986909 | A | -- | CYP3A4*13, decreased function of enzyme; involved in phase I detoxification of aflatoxin G1 |
| CYP3A4 | rs2740574 | C | -- | CYP3A4*1B, decreased function of enzyme; involved in phase I detoxification of aflatoxin G1 |
| CYP3A4 | rs4986910 | G | -- | CYP3A4*3, decreased function of enzyme; involved in phase I detoxification of aflatoxin G1 |
| CYP3A4 | rs4986907 | T | -- | CYP3A4*15A, decreased function of enzyme; involved in phase I detoxification of aflatoxin G1 |
| GSTM1 | rs366631 | A | -- | A/A: deletion (null) GSTM1 gene; increased risk of liver cancer with aflatoxin B1 exposure |
| GSTA1 | rs3957357 | A | -- | GSTA1*B, low/ non-functioning enzyme; increased risk of kidney disease with ochratoxin A exposure |
| GSTP1 | rs1695 | G | -- | G/G: reduced function, increased risk of liver damage with aflatoxin B1 exposure |
| SLCO1B1 | rs4149056 | C | -- | Increased risk of liver damage with aflatoxin B1 exposure |
| ADRA1A | rs1048101 | G | -- | G/G: This genotype may have fewer problems with reactions to patulin (theoretical); A/G and A/A: typical |
| GSDMB | rs7216389 | T | -- | increased risk of childhood asthma; 3-fold increased risk of asthma with known mold exposure |
| IL13 | rs20541 | A | -- | higher IgE levels; increased risk of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (fungal infection of the lung); increased risk of allergies, COPD |
Migraines: Curcumin has been shown to reduce inflammatory cytokines in the brain, including TNF-alpha. A clinical trial found that the combo of curcumin and CoQ10 effectively reduced the number of migraines.[ref][ref]Your migraine genes (see full article on Migraines):
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRPM8 | rs10166942 | C | -- | decreased risk of migraines (temperature and menthol receptor gene) |
| BDNF | rs6265 | T | -- | Increased risk of migraines due to lower BDNF |
| MMP16 | rs10504861 | T | -- | Reduced risk of migraines |
| NNMT | rs694539 | T | -- | TT only: 4-fold increase in migraine risk (methylation cycle) |
| MTHFR | rs1801133 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines (methylation cycle) |
| C7orf10 | rs4379368 | T | -- | Decreased risk of migraines (serotonin) |
| SLC6A4 | rs2066713 | A | -- | Decreased risk of migraines (serotonin) |
| AOC1 | rs1049793 | G | -- | Increased risk of migraines (histamines from foods) |
| AOC1 | rs10156191 | T | -- | Increased risk of migraines (histamines from foods) |
| TNF | rs3093664 | G | -- | Increased risk of migraines (inflammatory pathway) |
| TNF | rs1800750 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines (inflammatory pathway) |
| TNF | rs1800629 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines (inflammatory pathway) |
| IL1A | rs17561 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines (inflammatory pathway) |
| KCNK18 | rs869025175 | D | -- | rare mutation (talk with your doctor) |
| MTDH | rs1835740 | T | -- | This variant is linked to glutamate regulation. Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter. |
| LRP1 | rs11172113 | C | -- | Less likely to have migraines caused by cholesterol |
| NRP1 | rs2506142 | G | -- | 2-fold increased risk of menstrual migraine |
| PHACTR1 | rs9349379 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines |
| TRPV1 | rs8065080 | C | -- | C/T: more likely to have chronic migraines; C/C: protective against chronic migraines |
Depression and Inflammation:
A randomized clinical trial showed curcumin (500 mg/2x per day) to be more effective than a placebo for improving depression.[ref]
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF | rs1800629 | A | -- | Increased TNF-alpha |
| IL6 | rs1800796 | G | -- | GG only: Increased depression with inflammation |
| IL6 | rs1800795 | C | -- | CC only: Increased risk depression with stress |
| IL6 | rs1800797 | A | -- | Increased depression risk (Chinese pop.) |
| IL6R | rs4129267 | C | -- | CC only: Increased risk anxiety; depression |
| IL1B | rs16944 | G | -- | GG only: Increased IL1B; Increased risk depression |
| IDO1 | rs9657182 | C | -- | CC only: more likely to have depr. with inflammation |
| KMO | rs1053230 | T | -- | increased 3-OH-kynurenine, decreased risk of bipolar with psychosis (good) |
Precautions with curcumin:
Curcumin may increase oxalate excretion in the urine. People with genetic SNPs that increase susceptibility to kidney stones (or with a history of kidney stones) may want to consult their physician before starting curcumin.
Check your kidney stone variants.
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASR | rs1501899 | A | -- | Increased risk of kidney stones |
| UMOD | rs4293393 | G | -- | Increased risk of kidney stones |
| DGKH | rs4142110 | T | -- | Decreased risk of kidney stones |
| CLND14 | rs219780 | T | -- | Decreased risk of kidney stones |
| AGXT | rs34116584 | T | -- | Adds to hyperoxaluria risk; increased risk kidney stones |
| GRHPR | i5012629 | D | -- | Mutation for hyperoxaluria. (important) |
| GRHPR | i5012628 | D | -- | Mutation for hyperoxaluria. (important) |
| GRHPR | rs180177309 | D | -- | Mutation for hyperoxaluria. (important) |
| GRHPR | rs80356708 | D | -- | Mutation for hyperoxaluria. (important) |
| GOX1 | rs2235250 | T | -- | T/T: increased risk of oxalate kidney stones |
| AGTX | rs121908524 | A | -- | carrier of a primary hyperoxaluria mutation |
| AGTX | i5012625 | A | -- | carrier of a primary hyperoxaluria mutation |
| AGTX | rs121908527 | A | -- | carrier of a primary hyperoxaluria mutation |
| AGTX | i5001077 | A | -- | carrier of a primary hyperoxaluria mutation |
More articles that reference curcumin:
- Mercury detoxification: Curcumin increases the GLCM, the rate-limiting enzyme for glutathione production, which is important in mercury detoxification.[ref][ref]
- Fatigue: Curcumin inhibits TNF-alpha production.[ref]
- Diabetes and blood glucose genes: The curcumin-treated group had a decrease in HOMA-IR.[ref]
- PCOS genes: Curcumin decreased blood glucose levels as well as LDL cholesterol.[ref]
- Estrogen metabolism: Curcumin induces the expression of GSTP1 (glutathione S-transferase P1), which is important in estrogen metabolism.
- Boosting BDNF: Curcumin reverses the decrease in BDNF levels from chronic stress.[ref]
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Curcumin is beneficial in reducing inflammation in RA.[ref]
- IL-17 and Autoimmune Risk: Curcumin was found to decrease IL-17 (in an animal study).[ref]
- HMGB1 and Inflammasome activation: In animal studies, Curcumin inhibits HMGB1 release.[ref][ref]
- Osteoarthritis: A natural TNF-alpha blocker, curcumin has been shown in several studies to be effective for osteoarthritis.[ref][ref] A clinical trial found that curcumin (500mg / 3x per day) was as effective as diclofenac for osteoarthritis – but with fewer side effects.[ref]
- MRGPRX2 receptor on Mast Cells: Curcumin is likely a MRGPRX2 receptor blocker (animal and cell studies).[ref]
Berberine
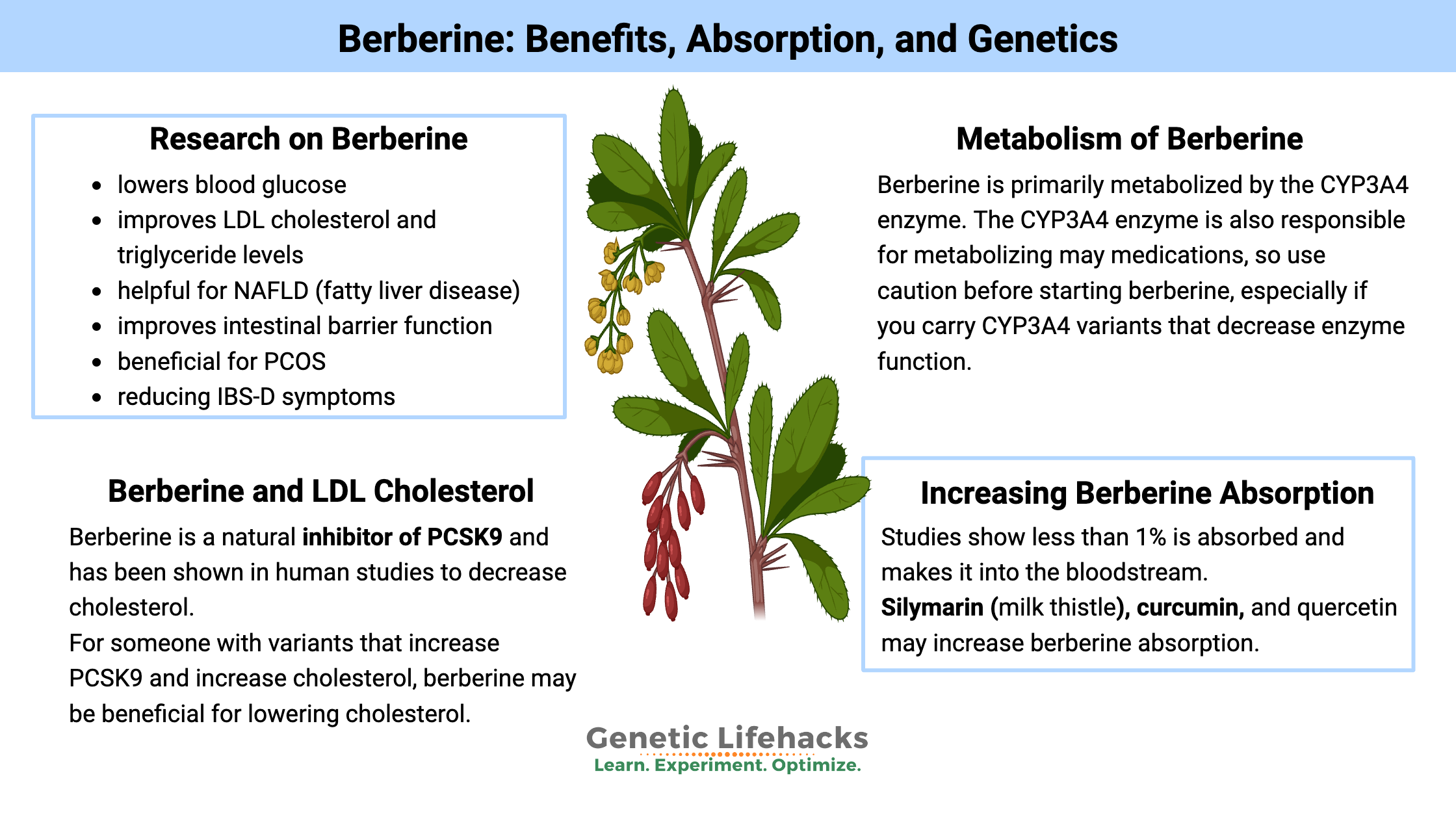
Berberine is a natural supplement with some amazing research for reducing high blood glucose levels and high cholesterol. The drawback, though, is poor absorption in the intestines, decreasing its effectiveness. Research on berberine shows:
- lowers blood glucose
- improves LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- helpful for NAFLD (fatty liver disease)
- improves intestinal barrier function
- beneficial for PCOS
- reducing IBS-D symptoms
Get the full article and details on berberine here.
Berberine may work well for:
Berberine is a natural inhibitor of PCSK9 and has been shown in human studies[ref][ref] and cell studies[ref] to decrease cholesterol.For someone with variants that increase PCSK9 and increase cholesterol (below), berberine may be beneficial for lowering cholesterol. Talk to your doctor, of course, if you have questions.
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCSK9 | rs11591147 | T | -- | Decreased LDL-cholesterol; lower risk of heart disease. (good) |
| PCSK9 | rs28362286 | A | -- | Decreased LDL-cholesterol; lower risk of heart disease. (good) |
| PCSK9 | rs67608943 | G | -- | Decreased LDL-cholesterol; lower risk of heart disease. (good) |
| PCSK9 | rs72646508 | T | -- | Decreased LDL-cholesterol; lower risk of heart disease. (good) |
| PCSK9 | rs505151 | G | -- | Increased LDL, increased risk of heart disease |
| PCSK9 | rs28942112 | C | -- | High LDL (important) |
| PCSK9 | rs28942111 | A | -- | High LDL (important) |
| PCSK9 | i5000370 | C | -- | High LDL (important) |
Berberine has been shown to decrease cholesterol levels as well as decrease Lp(a) levels.[ref][ref](Be sure to read the full article on Lp(a) if you have either of the first two variants.)
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPA | rs3798220 | C | -- | risk of elevated Lp(a), increased risk for heart disease (important) |
| LPA | rs10455872 | G | -- | risk of elevated Lp(a), increased risk for heart disease (important) |
| LPA | rs6919346 | T | -- | decreased Lp(a) |
| LPA | rs41272114 | T | -- | decreased Lp(a) |
| LPA | rs143431368 | C | -- | decreased Lp(a) |
| LPA | rs6415084 | T | -- | higher Lp(a) levels, increased risk of heart disease (Chinese population group); no increased risk in Iranian or European Caucasian populations |
Precautions with berberine:
Berberine uses CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 enzymes for metabolism. Thus, it may interact with medications that also use those enzymes. If you are on prescription medications, talk with your doctor before adding in a bunch of berberine.
Check your CYP2D6 genetic variants and check your CYP3A4 variants here.
The interaction with berberine may be important if you have slower CYP2D6 or CYP3A4 function – along with taking a medication that utilizes these enyzmes.
Researchers also caution that people with G6PD deficiency may have side effects from berberine.
Your G6PD gene variants (full article):
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G6PD | rs5030868 | A | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | rs72554664 | T | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | rs1050828 | T | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | rs72554665 | T | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | rs5030869 | T | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | rs137852327 | T | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | rs137852330 | A | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | i5012739 | T | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | i3003411 | T | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | i5008436 | T | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
| G6PD | i5008440 | A | -- | G6PD deficiency mutation |
More articles that reference berberine:
- NAFLD: Berberine (500mg, 3x per day) resulted in a more significant decrease in liver fat and a greater reduction in weight, HOMAR-IR, and lipid profiles.[ref]
- PCOS: Several randomized clinical trials have found that berberine is as effective as metformin for PCOS.[ref][ref]
- SCD1 and metabolism: Berberine decreases SCD1 levels and decreases fatty liver in animal studies.[ref][ref]
- Leptin: Improved leptin ratios and decreased BMI after three months of berberine (300mg/3x per day).[ref]
- Psoriasis: Berberine decreases psoriasis symptoms when used topically.[ref][ref]
Quercetin
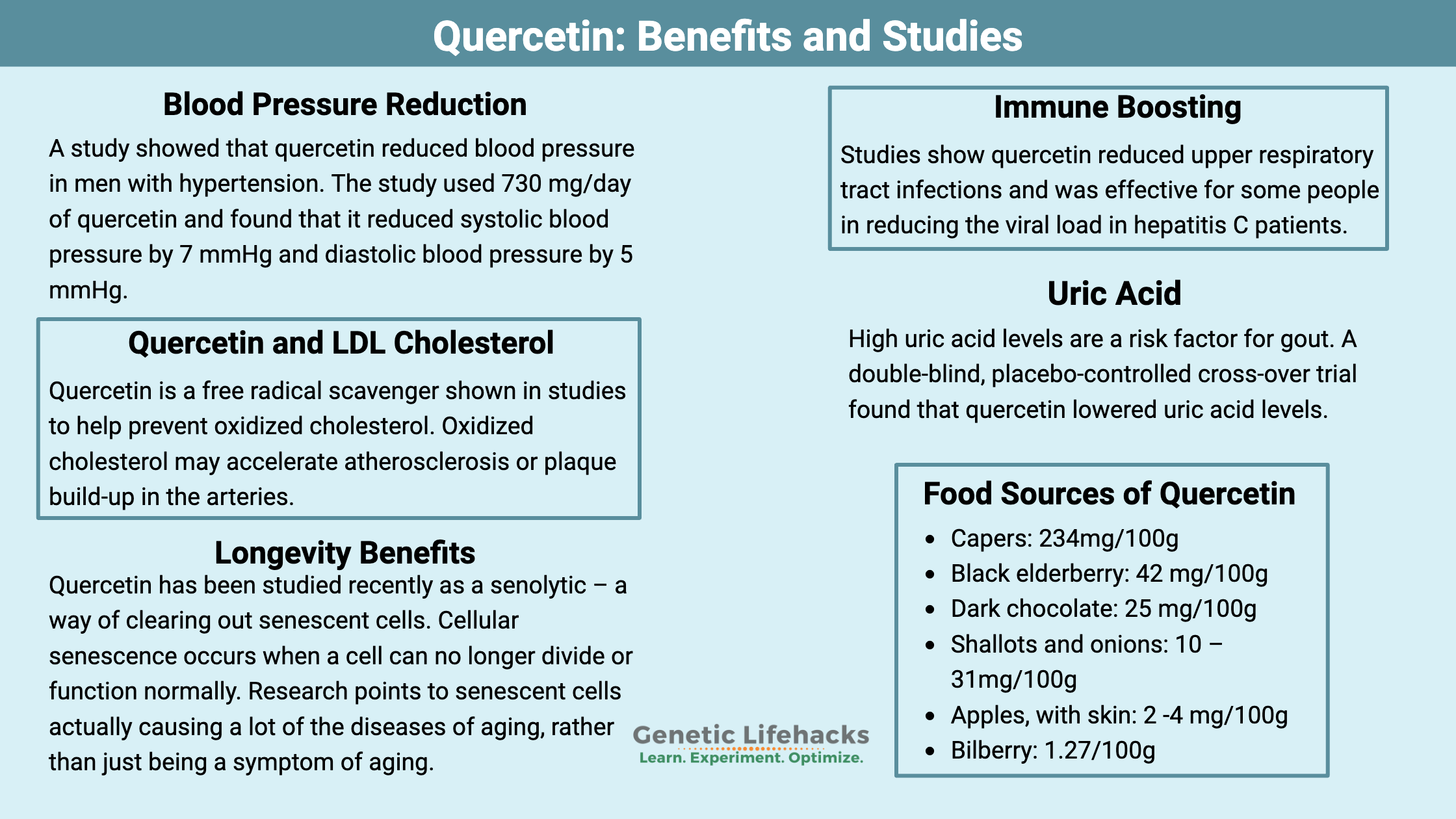
Quercetin is a natural flavonoid that acts as both an antioxidant and an anti-inflammatory. This potent flavonoid is found in low levels in many fruits and vegetables, including elderberries, apples, and onions. As a supplement, quercetin has many positive health benefits including:
- combating oxidative stress
- reducing blood pressure
- acting as a senolytic
- decreasing high uric acid levels
- reducing upper respiratory infections
- blocking mast cell activation
Detailed article on quercetin here.
Quercetin may work well for:
Quercetin stabilizes mast cells and inhibits histamine release.[ref]Histamine intolerance genes (Please read the full article for details):
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOC1 | rs10156191 | T | -- | Reduced production of DAO |
| AOC1 | rs2052129 | T | -- | Reduced production of DAO |
| AOC1 | rs1049742 | T | -- | Reduced production of DAO |
| AOC1 | rs1049793 | G | -- | Reduced production of DAO |
| AOC1 | rs2071514 | A | -- | possibly slightly higher DAO |
| HMNT | rs1050891 | A | -- | Reduced breakdown of serum histamine |
| HMNT | i3000469 | T | -- | Reduced breakdown of serum histamine |
| HMNT | rs2071048 | T | -- | T/T: Reduced breakdown of serum histamine (common) |
| HMNT | rs11558538 | T | -- | Reduced breakdown of serum histamine |
| HDC | rs2073440 | G | -- | Decreased histamine production |
| HDC | rs267606861 | A | -- | rare pathogenic mutation, linked to Tourettes |
| HRH1 | rs901865 | T | -- | Increased H1 receptor, increased asthma risk |
| HRH2 | rs2067474 | A | -- | Decreased H2 receptor |
| HRH4 | rs11662595 | G | -- | decreased HRH4 activation (receptor dysfunction), increased risk of progression in non-small cell lung cancer |
| MTHFR | rs1801133 | A | -- | MTHFR C677T, decreased enzyme function, affects methylation cycle |
| MTHFR | rs1801131 | G | -- | MTHFR A1298C, slightly decreased enzyme function, slightly affects methylation cycle |
A clinical trial using 500mg/day of quercetin for four weeks found that it decreased uric acid by 26·5 µmol/l on average.[ref]
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCG2 | rs2231142 | T | -- | Increased risk of gout; higher uric acid |
| ABCG2 | rs72552713 | A | -- | Increased risk of gout; higher uric acid |
| SLC2A9 | rs6449213 | C | -- | Decreased risk for gout; lower uric acid |
| SLC2A9 | rs7442295 | G | -- | Decreased risk for gout; lower uric acid |
| SLC2A9 | rs12510549 | C | -- | Decreased risk for gout; lower uric acid |
| SLC2A9 | rs12498742 | G | -- | Decreased risk for gout; lower uric acid |
| SLC2A9 | rs16890979 | T | -- | Decreased risk for gout; lower uric acid |
| SLC2A9 | rs1014290 | G | -- | Decreased risk for gout; lower uric acid |
| SLC2A9 | rs10805346 | T | -- | Decreased risk for gout; lower uric acid |
| SLC22A12 | rs475688 | C | -- | Higher risk of gout (common) |
| GCKR | rs780094 | T | -- | TT: higher risk of gout; CT and CC: lower risk of gout |
| SLC28A2 | rs2271437 | G | -- | Increased risk of gout |
Precautions with Quercetin:
COMT interaction:
Quercetin has a catechol structure and is partly metabolized through the COMT enzyme. If you carry the slower version of COMT, you may want to be careful and not go overboard with quercetin. This may be more important if taking more than one supplement that utilizes COMT (or at high doses).
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMT | rs4680 | A | -- | GG = higher activity; AG=Intermediate activity AA = lower activity |
| COMT | rs4633 | T | -- | CC = higher activity ; TT = lower COMT activity |
| COMT | rs6267 | T | -- | Minor decrease in COMT |
| COMT | rs165599 | A | -- | Minor decrease in COMT |
| COMT | rs165774 | A | -- | lower COMT activity; more likely to have irrational beliefs if subjected to maltreatment in childhood |
More articles that reference quercetin:
- Alopecia Areata: A mouse model of AA showed that quercetin stopped hair loss.[ref] Cell studies show that topical nano-particle quercetin holds promise for alopecia.[ref]
- NLRP3 inflammasome activation: Quercetin inhibits NLRP3 activation in cell and animal studies.[ref]
- Fatigue: Quercetin significantly inhibits IL-1B production.[ref]
- Inflammation and Depression: Animal studies show that quercetin effectively reduces depression and anxiety behavior.[ref][ref]
- Mast Cell Activation Syndrome Genes: Quercetin stabilizes mast cells and inhibits histamine release.[ref]
- APOE and Alzheimer’s Risk: Researchers theorize that oxidative stress contributes to Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Animal and cell studies show that quercetin can protect against oxidative stress in the brain and partially prevent the associated neuronal toxicity.[ref]
- Sirt3, Aging, and Mitochondrial Function: quercetin also has beneficial effects in part through the SIRT3 pathway.[ref][ref]
- Lipedema: Quercetin is another antioxidant supplement that researchers suggest as being a likely candidate to help with lipedema.[ref]
- Nickel Allergy: In patients with known nickel allergies, quercetin supplements for three days before nickel contact decreased their reaction by more than 50%.[ref]
- Cold Sores: Quercetin has been shown in cell studies to lower herpes simplex virus infectivity.[ref]
Hesperidin
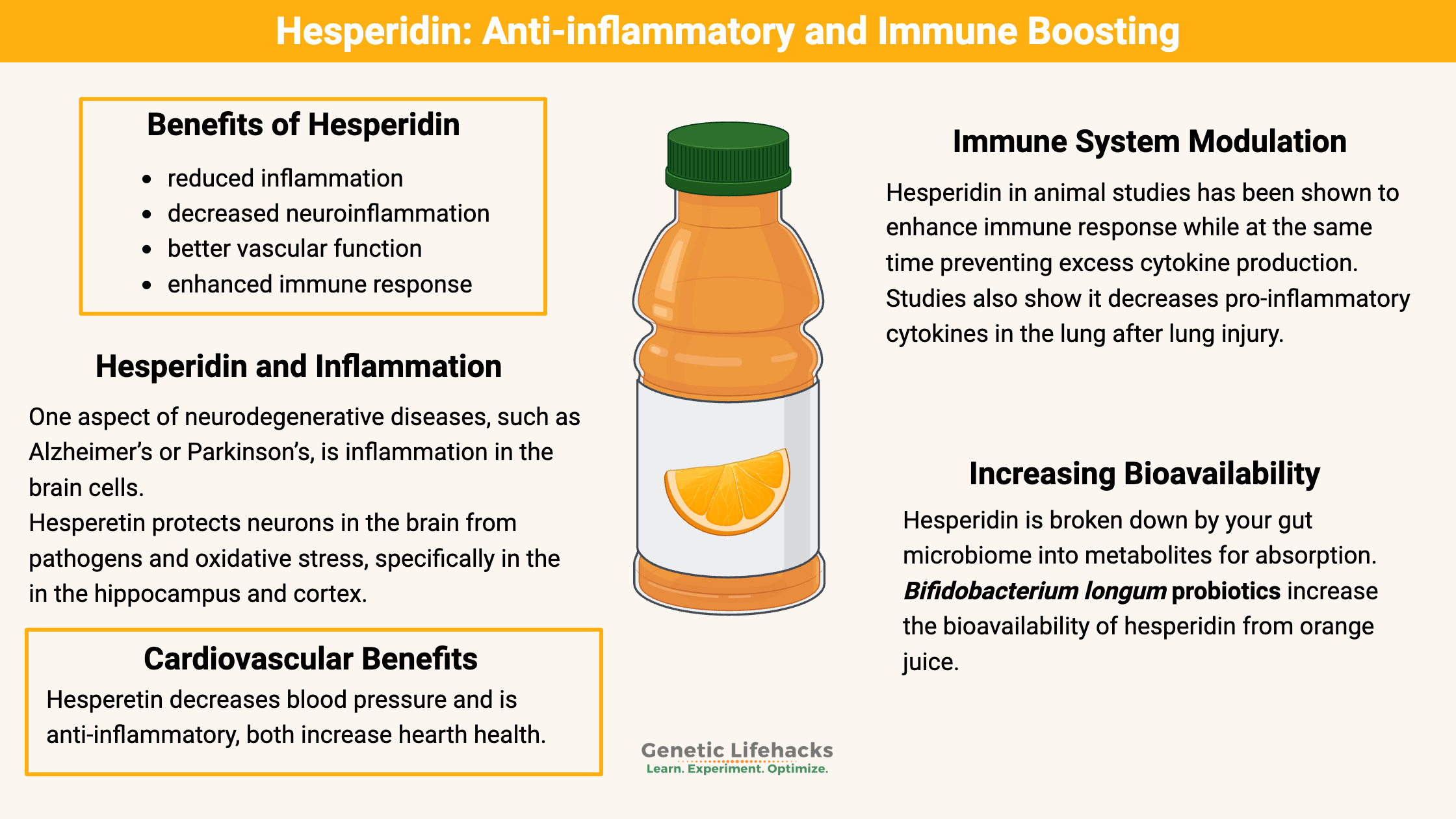
While not as well known as quercetin or curcumin, the research on hesperidin, a flavonoid found in citrus fruits, shows solid anti-inflammatory benefits — without interacting with slow COMT.
The benefits of hesperidin include:
- reduced inflammation
- decreased neuroinflammation
- better vascular function
- enhanced immune response
Hesperidin may work well for:
Hesperidin, a natural flavonoid from citrus fruits, inhibits the release of TNF-alpha.[ref][ref]
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF | rs1800629 | A | -- | Increased TNF alpha, increased risk of many chronic inflammatory diseases |
| TNF | rs361525 | A | -- | Increased TNF alpha, increased risk of many chronic inflammatory diseases |
| TNF | rs1799964 | C | -- | Increased TNF alpha, increased risk of many chronic inflammatory diseases |
| TNF | rs1799724 | T | -- | Increased TNF alpha, increased risk of many chronic inflammatory diseases |
| TNFRSF1A | rs1800693 | C | -- | Increased risk of multiple sclerosis; increased NF-kB signaling |
| TNFRSF1A | rs767455 | C | -- | Increased risk of inflammatory diseases. |
| TNFRSF1B | rs1061622 | G | -- | Increased risk of psoriasis, lupus |
| TNF | rs1800610 | A | -- | Lower TNF; less inflammation but more susceptible to infectious diseases |
Blocking TNF may benefit lupus patients with specific variants.
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-DQA1 | rs2187668 | T | -- | HLA-DRB1*0301. 2-fold increase in risk for lupus. |
| TNXB | rs1150754 | T | -- | 2-fold increase in lupus risk |
| TNF | rs1800629 | A | -- | Some increase in Lupus risk |
| TNFAIP3 | rs5029939 | G | -- | 2x Increased risk of lupus |
| STAT4 | rs7574865 | T | -- | Increased risk of discoid lupus |
| STAT4 | rs10181656 | G | -- | Increased risk of lupus |
| IRF5 | rs3807306 | T | -- | Increased risk of lupus |
| IRF8 | rs2280381 | C | -- | Decreased risk of lupus |
| IFIH1 | rs1990760 | T | -- | Increased risk of lupus |
| BLK | rs13277113 | A | -- | B lymphoid tyrosine kinase, increased risk of lupus |
| BLK | rs2248932 | A | -- | B lymphoid tyrosine kinase, increased risk of lupus |
| IRF5 | rs10954213 | A | -- | Increased risk of lupus |
| TLR7 | rs179010 | T | -- | Increased relative risk of lupus |
| SLC15A4 | rs1385374 | T | -- | Increased relative risk of lupus |
| SLC15A4 | rs1385374 | T | -- | Increased relative risk of lupus |
Cautions with hesperidin:
Hesperetin is an inhibitor of CYP2C9. If you have variants below, read more here, and then use caution when combining with medications that are metabolized through that pathway.
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP2C9 | rs1799853 | T | -- | CYP2C9*2 decreased function |
| CYP2C9 | rs1057910 | C | -- | CYP2C9*3 decreased function |
| CYP2C9 | rs2256871 | G | -- | CYP2C9*9 decreased function |
| CYP2C9 | rs9332131 | D | -- | CYP2C9*6 decreased function |
| CYP2C9 | rs28371685 | T | -- | CYP2C9*11 decreased function |
More articles that reference hesperidin:
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency: Hesperidin inhibits inflammation by blocking the release of TNF-alpha.[ref]
- Advanced Glycation End Products: Hesperidin can help upregulate glyoxalase 1, which may be helpful with AGEs. It does this by activating the Nrf2 pathway.[ref]
- Lipedema: A metabolite of hesperidin is recommended by researchers for lipedema, but there aren’t clinical trials on it yet.[ref][ref]
- Flu season: Hesperidin has been shown in several cell studies to inhibit the replication of influenza A. However, there aren’t any clinical trials of hesperidin for the flu.[ref]
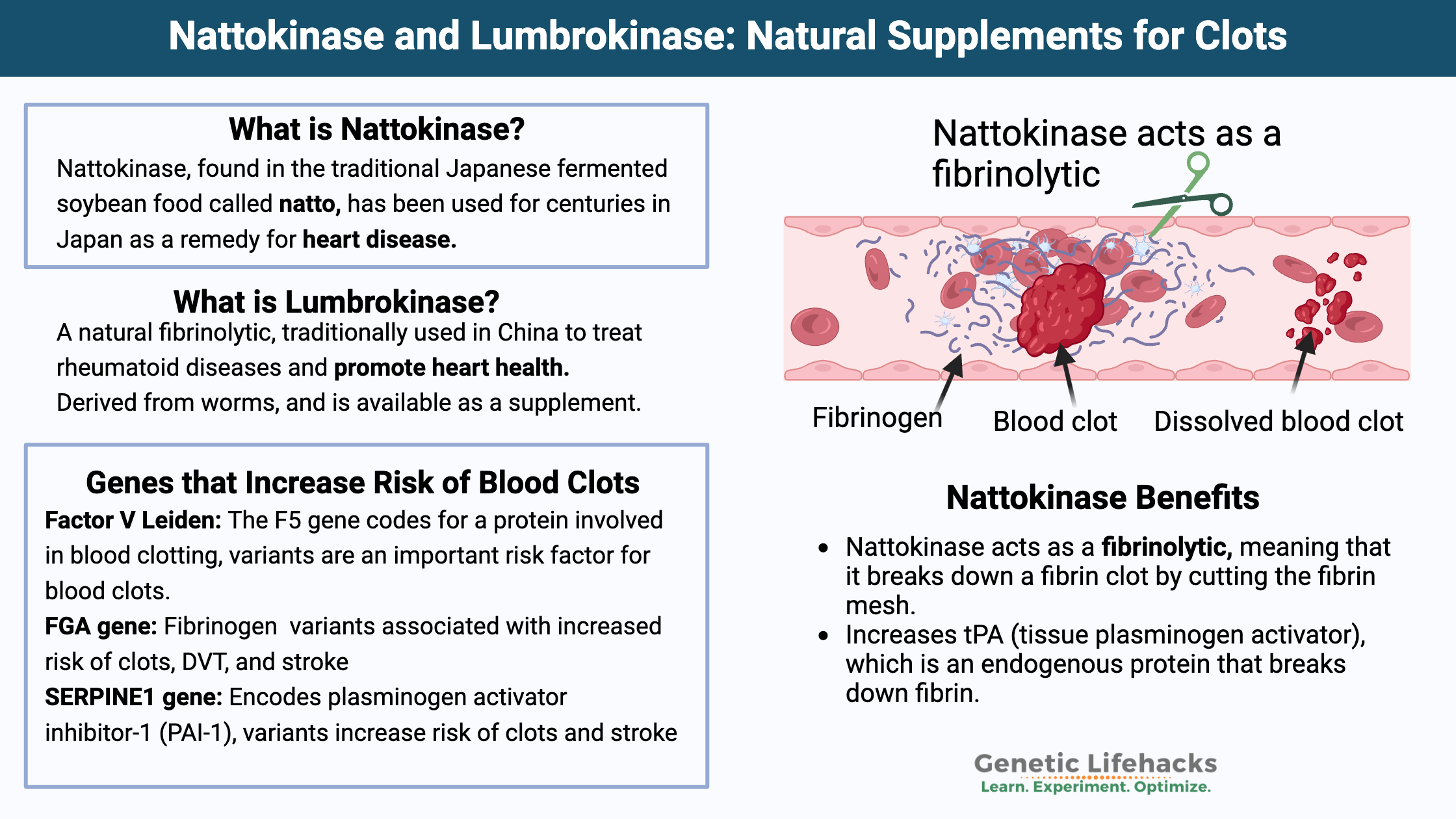
Nattokinase
A natural component of Japanese Natto, nattokinase is an enzyme that helps to break down blood clots. The full article is full of references and clinical trial data on nattokinase.
Detailed article on Nattokinase
Consider nattokinase for:
Nattokinase may be something to consider for anyone with variants related to higher fibrinogen levels
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGA | rs6050 | C | -- | Increased risk of stroke, DVT, heart disease |
| FGA | rs2070022 | A | -- | Decreased fibrinogen, lower clot risk |
| FGB | rs1800787 | T | -- | Increased fibrinogen, incr. stroke risk |
| FGB | rs1800789 | A | -- | Increased fibrinogen, incr. stroke risk |
| FGB | rs1800790 | A | -- | Increased fibrinogen, incr. stroke risk |
| FGG | rs2066865 | A | -- | Increased fibrinogen; increased risk for DVT |
| FGG | rs2066860 | T | -- | Slightly increased risk of DVT |
Clotting and microclots may factor in small fiber neuropathy.
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCN9A | rs6746030 | A | -- | increased risk of arthritis pain, back pain (lumbar disc), and phantom pain |
| SCN9A | rs4369876 | A | -- | More sensitive to pain, increased risk of small fiber neuropathy |
| SCN9A | rs74449889 | G | -- | Increased risk of neuropathic pain |
| SCN9A | rs80356470 | T | -- | (rare) primary erythromelalgia |
| SCN9A | rs182650126 | C | -- | (rare) increased risk of neuropathy pain |
| SCN10A | rs6795970 | A | -- | Higher pain threshhold; decreased pain in inflammatory bowel disease |
| SCN10A | rs12632942 | G | -- | GG: lower pain threshold |
| SCN10A | rs151090729 | T | -- | (rare mutation) hyperexcitable NaV1.8; increased risk of small fiber neuropathy |
| SCN11A | rs138607170 | A | -- | (rare mutation) familial episodic pain syndrome, hereditary autonomic neuropathy |
| SCN11A | rs483352921 | C | -- | (rare mutation) familial episodic pain syndrome |
| SCN11A | rs483352920 | G | -- | (rare mutation) congenital insensitivity to pain |
| SCN11A | rs141686175 | G | -- | (rare mutation) increased nerve firing, pain and neuropathy |
| TRPV1 | rs8065080 | C | -- | C/C: higher pain tolerance to pinprick pain (in Asian populations) |
Cautions with Nattokinase:
Please be sure to talk with your doctor if you are already on any anticoagulant or heart-related medications before taking nattokinase. Additionally, nattokinase is derived from natto, which is fermented. It is possible that people with histamine-related issues could notice an increase in histamine from nattokinase.
More articles that reference nattokinase:
- Factor V Leiden: Mutation in factor V increases the risk of aberrant clotting and DVTs.
CoQ10:
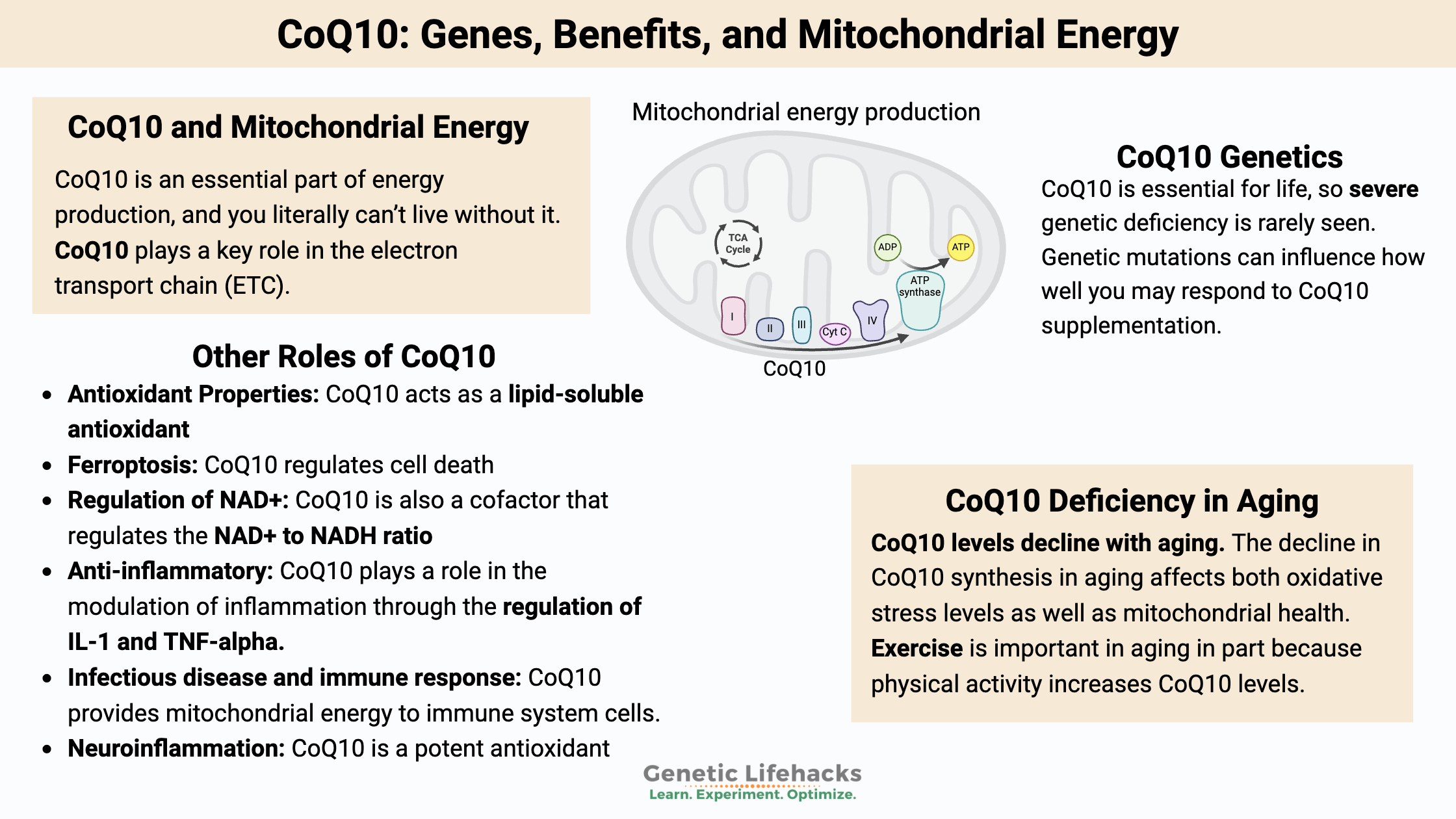
CoQ10 is used in cells as an antioxidant, immune modulator, and regulator of NAD+ — and for ATP production in the mitochondria. While many know about CoQ10 for heart health and mitochondrial energy, it is also important for:
- acting as a lipid-soluble antioxidant (prevent oxidized LDL)
- regulates cell death through ferroptosis
- acts as an anti-inflammatory by impacting IL-1 and TNF-alpha
- helps in the immune response against viruses and bacteria
Read the full CoQ10 article
Consider CoQ10 for:
In addition to lowering cholesterol, statins reduce CoQ10 levels. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials shows that CoQ10 levels are reduced in all types of statin users.[ref] [ref]
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMGCR | rs17244841 | A | -- | A/A: statins are more likely to work well in reducing LDL through inhibiting HMGCR |
| HMGCR | rs12916 | C | -- | C/C: less cholesterol-lowering response on moderate doses of statins |
| HMGCR | rs17238540 | T | -- | T/T: statins are more likely to work well in reducing LDL through inhibiting HMGCR |
| HMGCR | rs3846662 | G | -- | typical response to statins |
CoQ10 (400 mg/day) reduced the frequency and severity of migraines.[ref]
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRPM8 | rs10166942 | C | -- | decreased risk of migraines (temperature and menthol receptor gene) |
| BDNF | rs6265 | T | -- | Increased risk of migraines due to lower BDNF |
| MMP16 | rs10504861 | T | -- | Reduced risk of migraines |
| NNMT | rs694539 | T | -- | TT only: 4-fold increase in migraine risk (methylation cycle) |
| MTHFR | rs1801133 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines (methylation cycle) |
| C7orf10 | rs4379368 | T | -- | Decreased risk of migraines (serotonin) |
| SLC6A4 | rs2066713 | A | -- | Decreased risk of migraines (serotonin) |
| AOC1 | rs1049793 | G | -- | Increased risk of migraines (histamines from foods) |
| AOC1 | rs10156191 | T | -- | Increased risk of migraines (histamines from foods) |
| TNF | rs3093664 | G | -- | Increased risk of migraines (inflammatory pathway) |
| TNF | rs1800750 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines (inflammatory pathway) |
| TNF | rs1800629 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines (inflammatory pathway) |
| IL1A | rs17561 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines (inflammatory pathway) |
| KCNK18 | rs869025175 | D | -- | rare mutation (talk with your doctor) |
| MTDH | rs1835740 | T | -- | This variant is linked to glutamate regulation. Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter. |
| LRP1 | rs11172113 | C | -- | Less likely to have migraines caused by cholesterol |
| NRP1 | rs2506142 | G | -- | 2-fold increased risk of menstrual migraine |
| PHACTR1 | rs9349379 | A | -- | Increased risk of migraines |
| TRPV1 | rs8065080 | C | -- | C/T: more likely to have chronic migraines; C/C: protective against chronic migraines |
Precautions with CoQ10:
Talk with your doctor if you are on warfarin or statins and have concerns about interactions with CoQ10.
More articles that reference CoQ10:
- Egg Quality when TTC: CoQ10 may be helpful in improving egg quality for women trying to get pregnant.
- Migraine prevention: CoQ10 (400 mg/day) reduced the frequency and severity of migraines.[ref]
- Fatigue (ME/CFS): Supplementing with 150mg of ubiquinol, a form of CoQ10, improved cognitive function in people with CFS/ME.[ref]
- Inclusion Body Myositis: CoQ10 and carnitine may help reduce symptoms for some individuals.[ref]
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN)
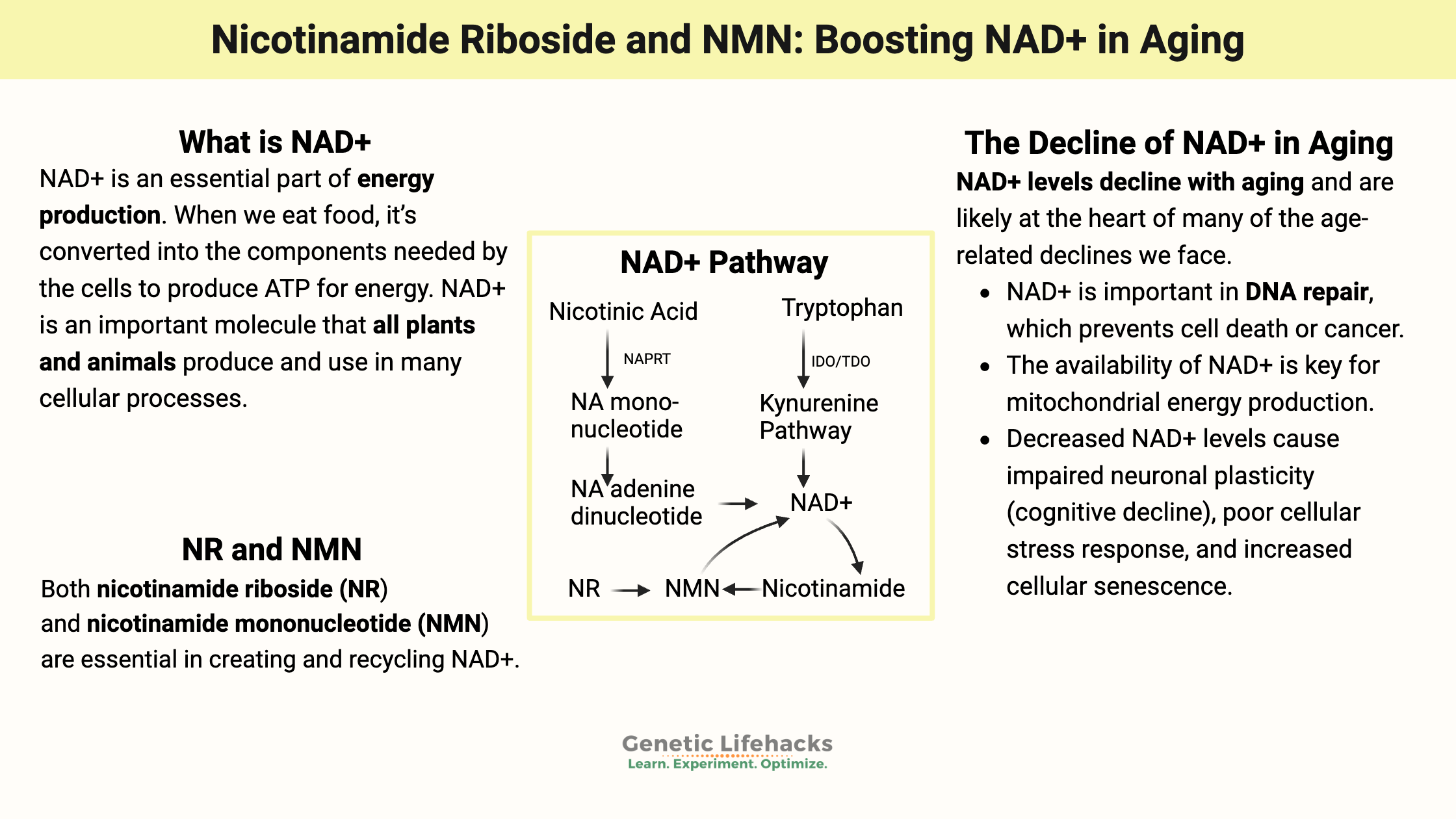
NAD+ is an essential part of mitochondrial energy production. As we age, our NAD+ levels decline, and researchers believe this may tie into a lot of chronic diseases related to aging. NR and NMN are supplements that can increase NAD+ levels.
Read the full article on Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN)
Consider NR or NMN for:
Several studies have shown that NMN or NAD+ precursors restore fertility at the end of an animal’s normal reproductive age. It seems to do this through rejuvenating egg quality.[ref]
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTHFR | rs1801133 | A | -- | MTHFR C677T; reduced folate enzyme efficiency |
| MTHFR | rs1801131 | G | -- | MTHFR A1298C; reduced folate enzyme efficiency |
| F5 | rs6025 | T | -- | Factor V Leiden; increased clot risk and miscarriage risk |
| F2 | rs1799963 | A | -- | Prothrombin variant; increased risk of clots and miscarriage |
| LHCGR | rs13405728 | G | -- | Luteinizing hormone and hCG receptor; Increased risk of PCOS |
| LHCGR | rs2293275 | T | -- | Luteinizing hormone and hCG receptor; Increased risk of PCOS |
| DENND1A | rs10818854 | A | -- | Increased androgen synthesis; Increased risk of PCOS |
| FSHB | rs11031006 | A | -- | Increased lutenizing hormone to FSH ratio |
| FSHR | rs6166 | C | -- | Folicle-stimulating hormone receptor; Increased PCOS risk |
| ADIPOQ | rs2241766 | G | -- | lower risk of PCOS (good); T/T has higher risk of PCOS which can impact fertility |
| ADIPOQ | rs1501299 | T | -- | TT: Decreased risk of PCOS (good) |
| MTNR1B | rs10830963 | G | -- | Melatonin receptor in pancreas; increased risk of PCOS and higher insulin levels |
| F2 | i3002432 | A | -- | Prothrombin variant; increased risk of clots and miscarriage |
Cell and animal studies show that NMN decreases inflammation while promoting healing in tendons.[ref]
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COL1A1 | rs1800012 | A | -- | A/A: significantly reduced risk of Achilles’ tendon tear (good) |
| COL5A1 | rs12722 | T | -- | higher risk of Achilles’ tendinopathy (lower levels of COL5A1); increased risk of tennis elbow |
| MIR608 | rs4919510 | G | -- | Associated with chronic Achilles' tendinopathy |
| BMP4 | rs2761884 | T | -- | Increased risk of tendinopathies |
| FCRL3 | rs7528684 | G | -- | Increased risk of tendinopathies |
| TNF | rs1800629 | A | -- | Higher TNF-alpha levels; increased risk of Achilles tendon problems and knee tendon problems |
| MMP13 | rs2252070 | T | -- | Increased risk of posterior tibial tendon problems (flat foot) |
| MMP1 | rs1144393 | C | -- | Increased risk of posterior tibial tendon problems (flat foot) |
| MMP3 | rs650108 | G | -- | G/G: increased risk of tendinopathies (athletes) |
| MMP3 | rs679620 | T | -- | T/T: increased risk of tendinopathies (athletes) |
| GDF5 | i6011281 | A | -- | A/A: higher risk of achilles tendon (common genotype) |
| GDF5 | rs143383 | A | -- | A/A: higher risk of achilles tendon (common genotype) |
Precautions with NR or NMN:
The research is not totally clear on whether NR or NMN could promote cancer growth. I would err on the side of caution until the research is conclusive if I was battling cancer.
NAD+ levels decline significantly with age. Research doesn’t show a benefit for taking NR or NMN in people who are young and healthy since they are likely to have sufficient NAD+ already.
More articles that reference NR and NMN:
- Long Covid: AgelessRX has a clinical trial underway using low-dose naltrexone and nicotinamide riboside.[ref]
- Depression and Mitochondrial Function: Nicotinamide riboside (NR) reduces inflammation in the brain and improves cognitive function in animal studies.[ref]
- Inclusion Body Myositis: A recent study (Jan. 2021) showed that increasing NAD+ levels via nicotinamide riboside may help with mitochondrial muscle function. The study used animal and cell models (not a randomized trial).[ref]
Creatine
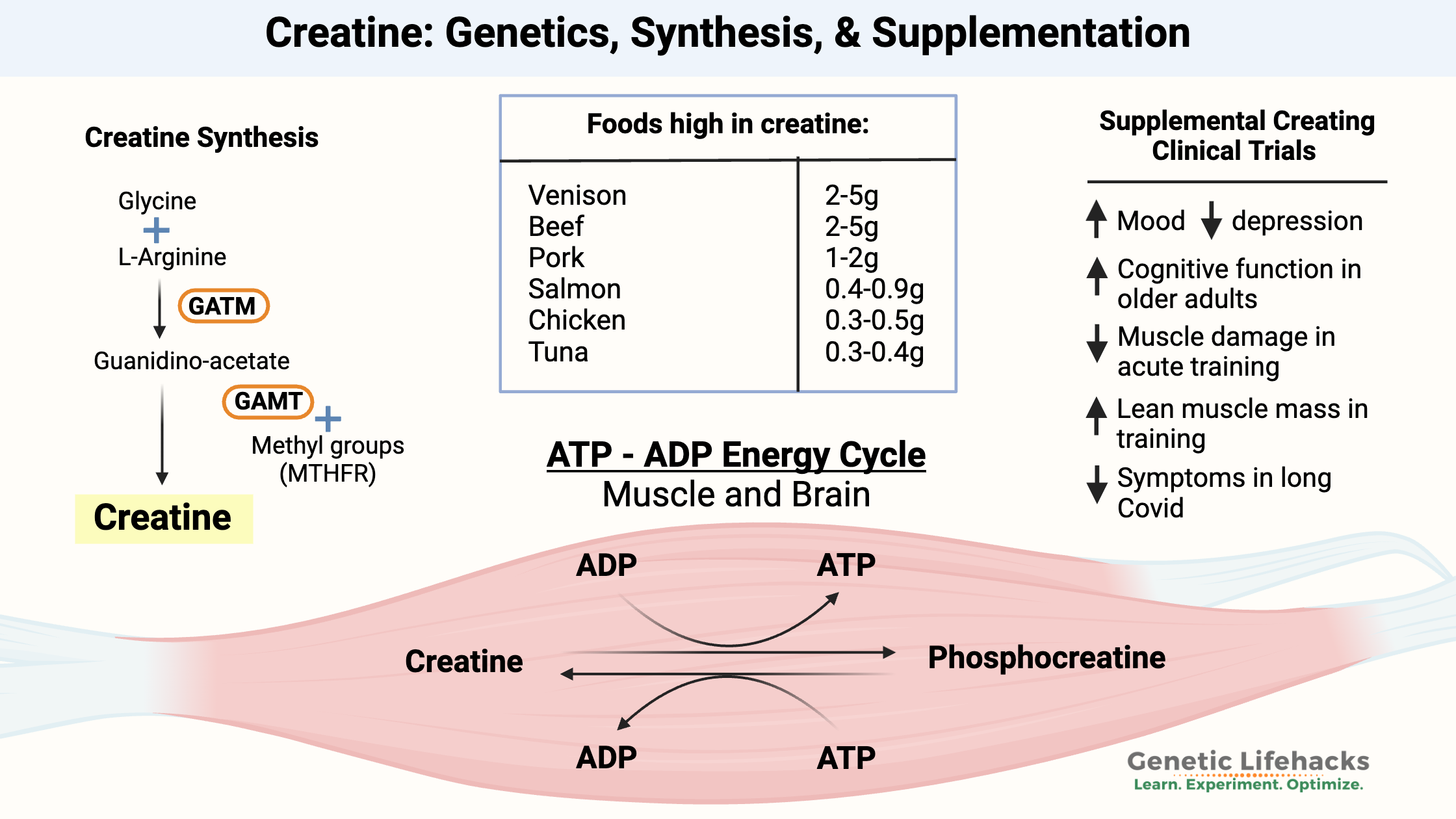
Creatine is an amino acid important in energy production in brain tissue and muscles. It is produced from a reaction that includes the amino acids glycine and arginine, along with a methyl group.
Read the full article on creatine
Consider creatine for:
Creatine synthesis genetic variants: Genetic variants can impact how your cells make creatine.
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GATM | rs1346268 | C | -- | reduced risk of muscle pain with statins; likely higher levels of GATM |
| GATM | rs80338737 | A | -- | rare mutation linked to Arginine:glycine amidinotransferase deficiency |
| CKM | rs8111989 | C | -- | found in higher frequency in elite combat sport athletes; slightly better physical performance; possibly more creatine kinase |
| CKM | rs11559024 | C | -- | decreased creatine kinase levels |
| CKM | rs4884 | G | -- | protective against knee osteoarthritis (good) |
MTHFR:
The MTHFR gene encodes an enzyme that is important in the methylation cycle and production of methyl groups. A methyl group is needed for the synthesis of creatine, so for people who have limitations on the methylation cycle, supplemental creatine may help take the strain off the pathway.
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTHFR C677T | rs1801133 | A | -- | 40-70% decrease in MTHFR enzyme function (folate metabolism) |
| MTHFR A1298C | rs1801131 | G | -- | 10-20% decrease in MTHFR enzyme function (folate metabolism) |
High homocysteine:
Supplemental creatine can help to lower homocysteine levels in healthy people with good kidney function.[ref][ref][ref]
| Gene | RS ID | Effect Allele | Your Genotype | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTHFR | rs1801133 | A | -- | MTHFR C677T, higher homocysteine levels, especially if folate is lacking |
| NOX4 | rs11018628 | C | -- | decreased homocysteine, decreased stroke risk |
| MTR | rs1805087 | G | -- | increased risk of cognitive impairment due to higher homocysteine |
| MTR | rs2275565 | T | -- | associated with higher homocysteine levels |
| MTRR | rs1801394 | G | -- | somewhat increased homocysteine levels, especially if riboflavin is low |
| CBS | rs5742905 | G | -- | risk of increased homocysteine, responsive to vitamin B6 |
| PON1 | rs662 | C | -- | higher homocysteine-thiolactone levels |
| PEMT | rs7946 | T | -- | TT: homocysteine increases with low folate diet |
| BHMT | rs3733890 | A | -- | reduced conversion of choline to betaine |
Cautions with creatine:
Creatine is used in clinical trials without side effects, but there are cautions for people with kidney disease. Talk with your doctor if you have any health concerns with creatine.
More articles that reference creatine:
- AMPD1 deficiency:
Creatine supplements have been used to prevent muscle soreness in people with AMPD1 deficiency. Studies have shown varying results for the impact of creatine.[ref][ref] - Mood or depression:
Clinical trials show creatine may help with depression caused by a lack of brain energy or oxidative stress.[ref]