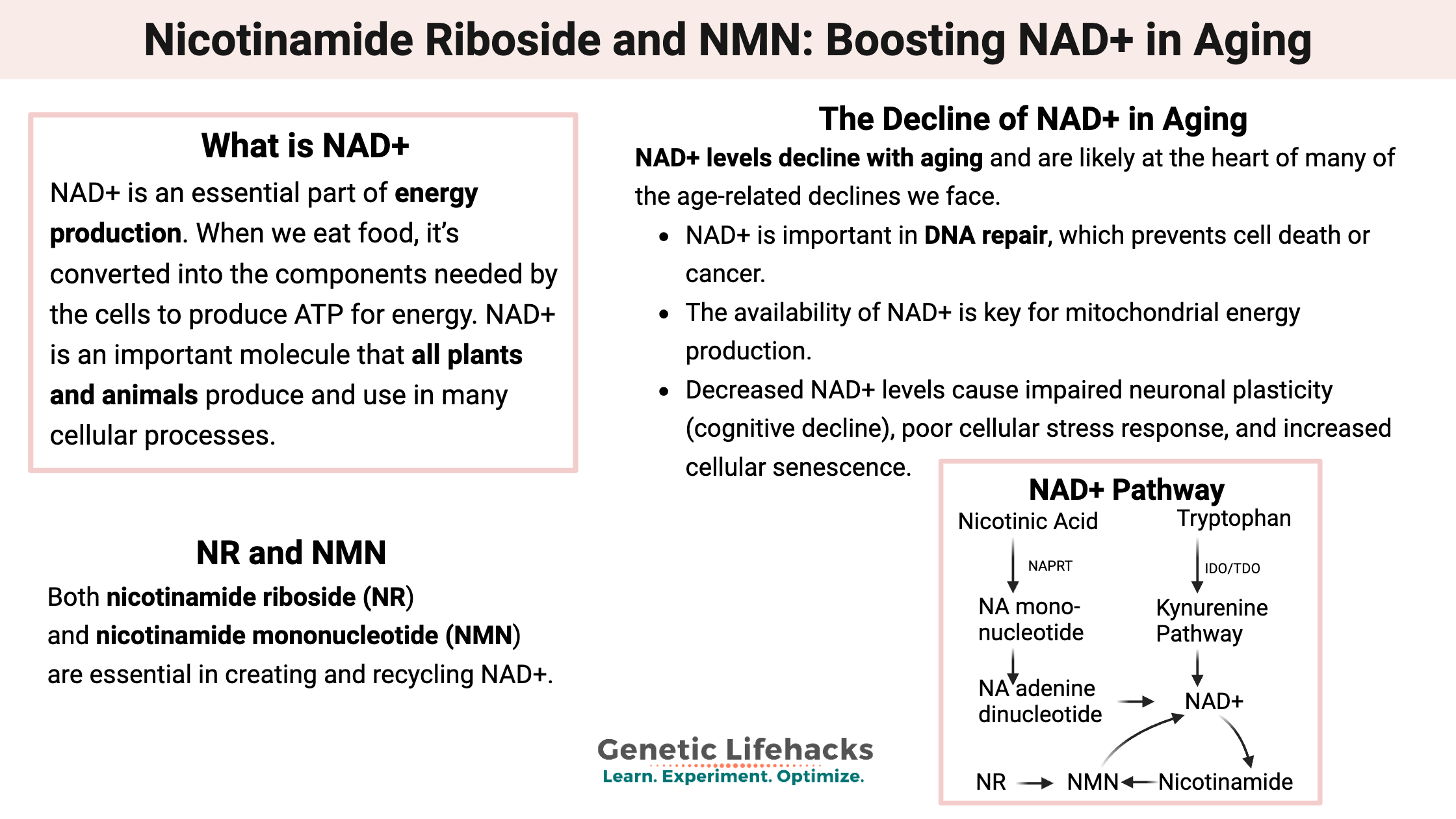
Nicotinamide Riboside and NMN: Boosting NAD+ in Aging with Supplements
Explore the research about how nicotinamide riboside (NR) and NMN are being used to reverse aging. Learn about how your genes naturally affect your NAD+ levels and how this interacts with the aging process.