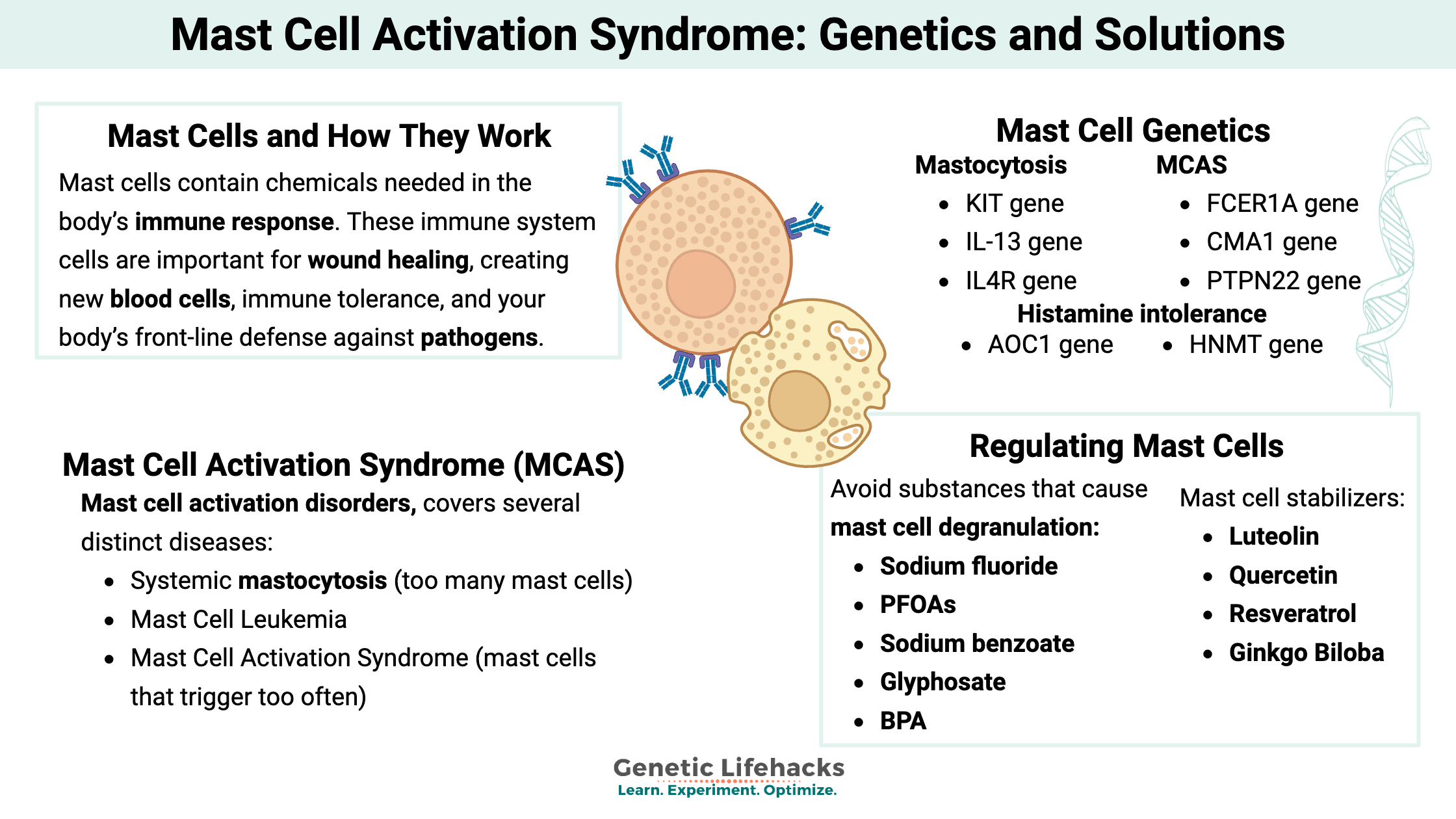
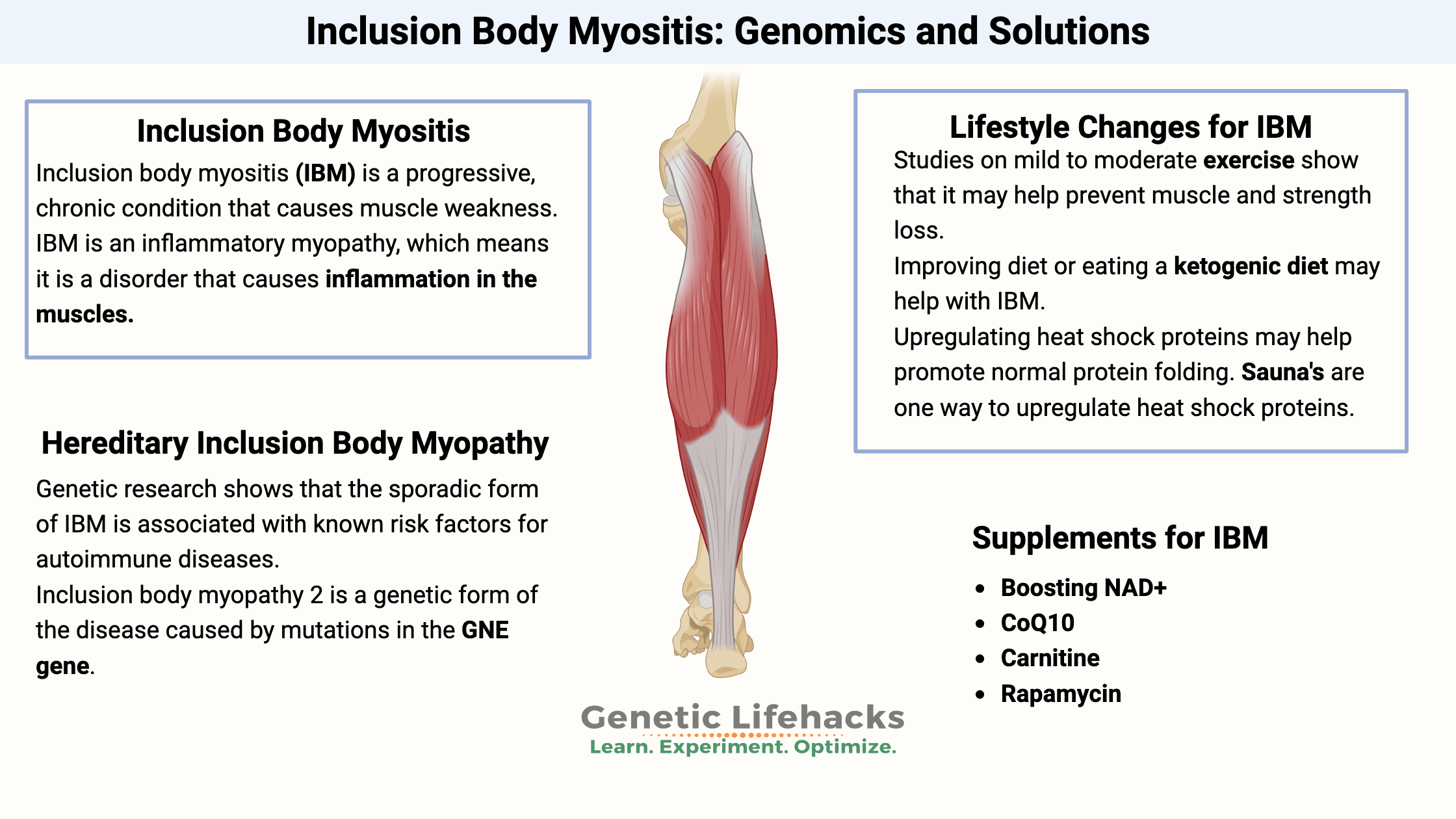
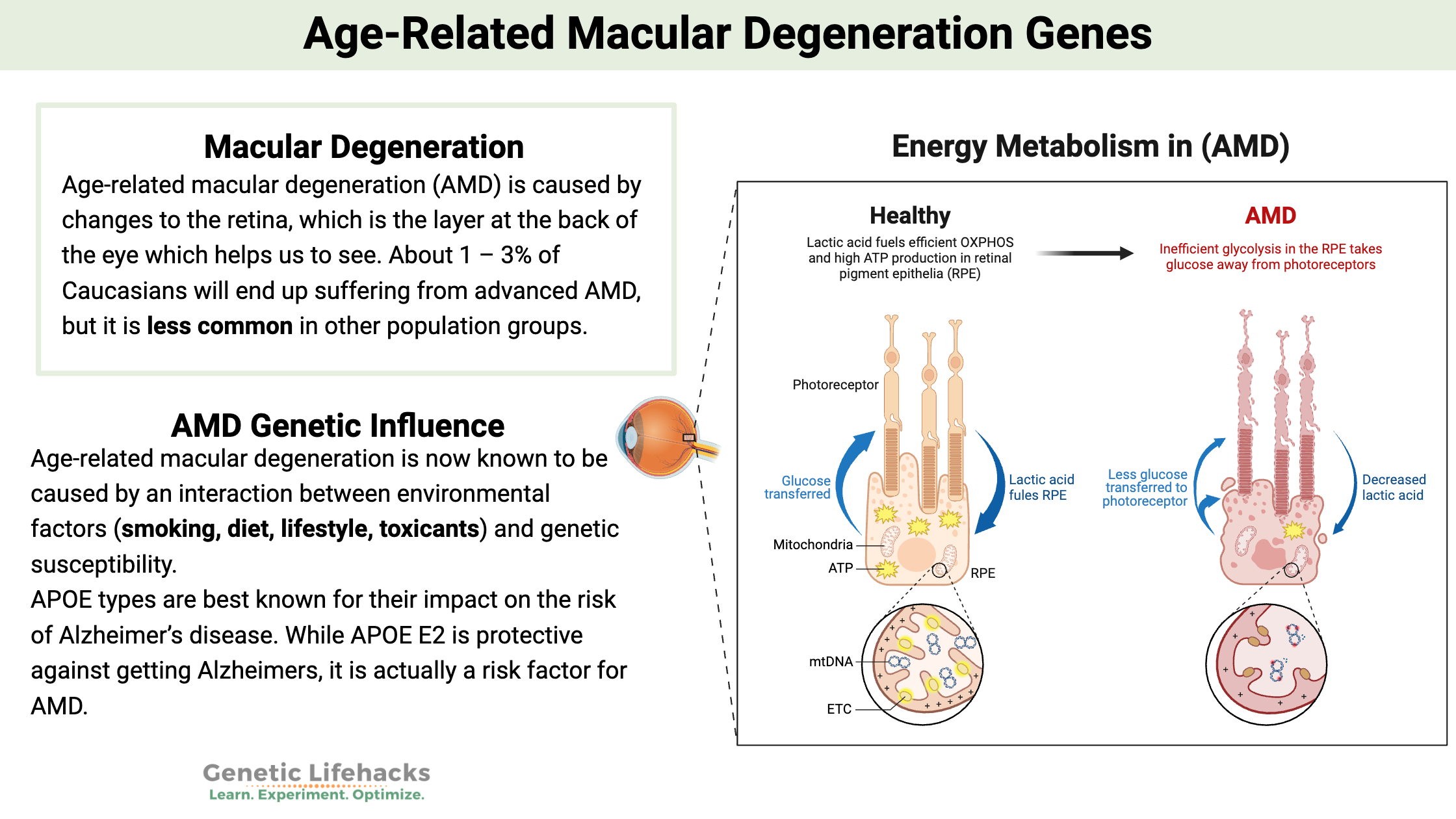
Mast Cells: MCAS, Genetics, and Solutions
Mast cells are essential to your innate immune system, defending against pathogens and allergens. For some people, mast cells can be triggered too easily, giving allergy-like responses to lots of different substances.